The preventive test of electrical equipment insulation is an important measure to ensure the safe operation of equipment. This paper analyzes and discusses the various characteristics of electrical equipment insulation from four test methods to judge the defects inside the insulation.

1 measurement of insulation resistance
The most basic and commonly used non-destructive test method is to measure the insulation resistance with a megger. Generally, the insulation of electrical equipment is multi-layered. These multilayer insulators have an absorption phenomenon when external DC voltage is applied, that is, the current gradually decreases and tends to a certain constant value (leakage current). Because the current passing through the medium is inversely proportional to the measured value of the dielectric resistance, if the insulation condition of the test object is better, the absorption process proceeds more slowly, and the absorption phenomenon becomes more obvious, such as the sample is heavily wetted or has concentrated conductive channels therein. Since the insulation resistance is significantly reduced, the leakage current is increased, and the absorption process is fast, so that the current flowing through the insulation rapidly becomes a large leakage current. Therefore, the insulation state of the test article can be judged based on the current change of the test article.
When there is a concentrated defect in the insulation of the test article, the insulation resistance reflecting the leakage current is significantly reduced, and it is found when it is inspected by a megohmmeter. For example, the most common defect of pin insulators in substations is porcelain cracking. After cracking, the insulation resistance drops significantly. Generally, it can be detected by a megohmmeter. The insulation of the generator often changes greatly, and it is the volume of the test object. Dimensions, air conditions, etc., it is often difficult to give a certain standard of insulation resistance. It is common to compare the insulation resistance of different phases under the same operating conditions, or to compare the measured insulation resistance with the insulation resistance value it has measured in the past; for larger equipment such as motors, Transformers, capacitors, etc. can use absorption phenomena to measure their insulation resistance (ie, insulation resistance measurements) over time to determine insulation conditions. The absorption test reflects the local defects and moisture levels of Class B insulation and Class B dip insulation. The absorption of the stator insulation of the generator is very obvious and is usually expressed by the absorption ratio K (ie the ratio of the 60 s ohmmeter reading to the 15 s reading). Since the value of K is the ratio of the two insulation resistances, it is not related to the size of the equipment, which can be used to reflect the insulation state. The insulation is intact and the absorption phenomenon is obvious. The absorption ratio is often larger than K (greater than 1.3). When the insulation is wet, the absorption phenomenon is not Obviously, the absorption is relatively small (close to 1).
It should be noted that sometimes when some concentrated defects have developed so badly that they are broken down in the withstand voltage test, the insulation resistance and absorption ratio measured before the withstand voltage test are high, because Although these defects are serious, they have not been penetrated. Therefore, it is impossible to judge the insulation condition only by the measurement of the insulation resistance, and other methods need to be selected for the test.
2 leakage current test
The leakage current test has the same principle as the insulation resistance measurement, except that the former is carried out at a higher voltage (above 10kV). Usually, the leakage current of the sample under different test voltages is measured, and the relationship between the leakage current I and the test voltage U is made. The curve thus makes it possible to detect the defects found more sensitively. For good insulation, the leakage current rises linearly with the test voltage, and the value is small; when the insulation is wet or there is a concentrated defect in the insulation, the leakage current value will increase sharply when the test voltage exceeds a certain test voltage, and the more serious the defect, the leakage value The lower the test voltage that is exploding, the risk of breakdown during operation of the device.
The leakage current value measured by the equipment can be compared according to the regulations, and the analysis is judged by referring to the past records.
3 Measurement of dielectric loss tangent (tgδ)
This is a method that is used more and is more effective in judging insulation. By measuring tgδ, it can reflect the distribution defects of the whole insulation, such as the general moisture and aging of the insulation during operation (such as oil degradation, aging of organic solid materials, etc.) At this time, the active current component flowing through the insulation increases, and tgδ also increases, which actually reflects the increase in power loss per unit volume in the insulation. Checking transformers, transformers, bushings, capacitors, etc. with the method of measuring tgδ has certain effects.
If the defects in the insulation are not distributed but concentrated, the measured tgδ method sometimes reflects insensitivity, and the larger the insulation volume of the test, the less sensitive it is.
For electrical equipment such as motors and cables , the faults in operation are mostly caused by the development of concentrated defects. The larger the whole volume, the worse the effect of measuring tgδ. Therefore, this test is usually not carried out when conducting preventive tests on motors, cables and other equipment in operation. For casing insulation, the tgδ test is an indispensable and effective test. Because of the small size of the casing, the tgδ test not only reflects the insulation distribution of the casing, but also sometimes detects its concentrated defects.
When judging the insulation condition by the tgδ method, it is necessary to compare it with the tgδ value of the previous year and compare it with other equipment of the same type under the same operating conditions. Even if tgδ does not exceed the standard, it must be significantly increased compared with the past. Handle to avoid accidents during operation.
The test methods mentioned above are all carried out at a lower voltage and are non-destructive tests. Through comprehensive comparative analysis by test, the insulation condition and defect properties of the equipment under test can be judged. The insulation preventive test is generally performed once a year. If it is found in the test that it is inconsistent with the regulations, the cause should be identified and the defect should be eliminated.

4 withstand voltage test
The withstand voltage test is an important item of the insulation preventive test, that is, applying a voltage higher than the operating voltage to the insulation for the withstand voltage test. It may also cause damage to the insulation of the equipment during the test, so it is also called destructive test. In order to avoid damage to the equipment, the withstand voltage test is to be carried out after the non-destructive test. At present, the application of withstand voltage test methods in the insulation preventive test mainly includes: AC withstand voltage and DC withstand voltage. In the test, a large number of defects were found, which effectively improved the safety of electrical equipment.
1) AC withstand voltage test
AC withstand voltage test can effectively find more dangerous concentrated defects, can accurately test the insulation margin, but has an important disadvantage: that is, for solid organic insulation, when the high AC voltage acts, it will make some insulation The weakness is more developed, so the appropriate test voltage should be chosen. It is generally considered that the variation of the withstand voltage test voltage during operation should be lower than the factory voltage. And equipment in different situations should be treated differently. For example, the test voltage of the stator winding of the generator before the overhaul is usually 1.3 to 1.5 times the rated voltage; for the generator that has been running for more than 20 years, due to the older insulation, the rated voltage of 1.3 times can be taken for the withstand voltage test. However, for a generator that has been directly connected to an overhead line for more than 20 years, it is considered that the atmospheric overvoltage attack may be large during operation, and it is still required to use a 1.5 times rated voltage for the withstand voltage test for safety. When doing the withstand voltage test, it is often boosted to the test voltage, pressurized for 1 min to observe the condition of the test article, and at the same time, to expose the defect that has begun to break down, the withstand voltage should not be too long to avoid insulation. A breakdown has occurred.
2) DC withstand voltage test
The DC withstand voltage test can also determine the electrical strength of the insulation. Compared with the AC withstand voltage test, it is characterized by: the test equipment is light and small, and secondly, while the insulation is subjected to the DC withstand voltage test, the leakage current can be measured to observe the internal Insulation defects.
The selection of the DC withstand voltage test voltage should also refer to the ratio of the power frequency AC withstand voltage test voltage and the AC/DC breakdown strength of the insulation. Take 2~2.5 times of rated voltage for generator stator winding, 5~6 times rated voltage for 3,6,10kV power cables ; 4~5 times rated voltage for 20~35kV cables; 3 times for 35kV cables Rated voltage. The power cable is subjected to a DC withstand voltage test for 5 minutes, and the leakage current reading is used to find the defect. The DC withstand voltage is longer than the AC withstand voltage. Therefore, the generator test is to increase in stages by 0.5 times the rated voltage of each stage, and each stage stays for 1 min to observe and read the leakage current value. The use of DC high voltage to test the withstand voltage of electrical equipment is of more significance.
In order to ensure that electrical equipment can operate safely and reliably, preventive measures should be taken regularly for insulation, and latent defects should be detected through some tests.
This product response time is shorter than resistive tonch screen's with a good touch.It is widely used to Phone,Tablet,E-book,gaming device by hands holding,Touch Monitor,GPS,All-In-One and so on.GreenTouch projected capacitive touch technology is with fast and sensitive response, the design with frame (without frame is optional) makes it looks professional and generous. The model is designed for high-intensity and high-frequency business environments.
Product show:
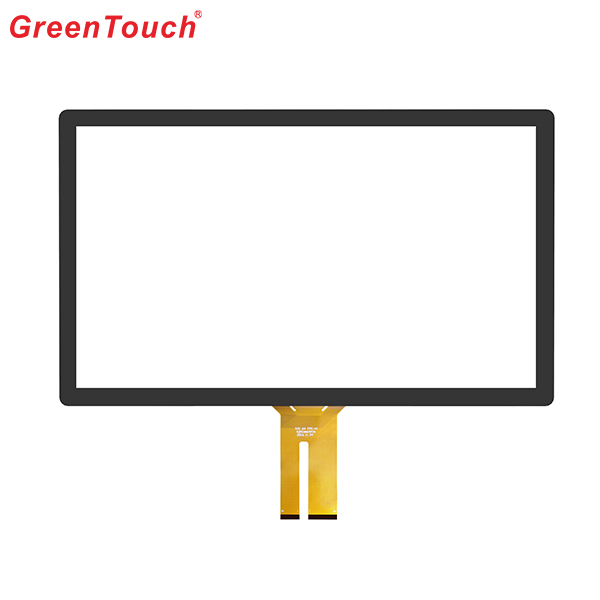
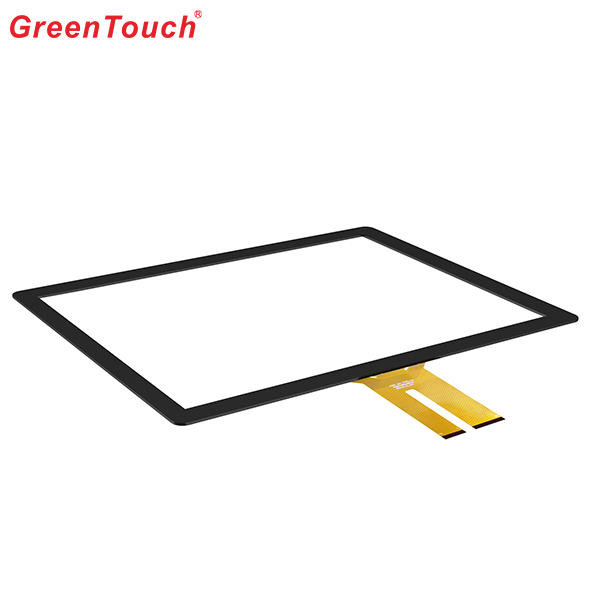
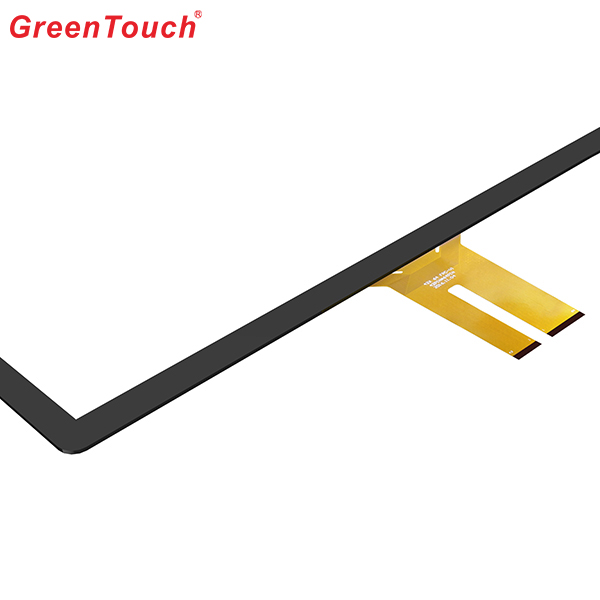


Capacitive Touch Screen Panel,Android Touch Screen,Portable Touch Screen,Pcap Touch Screen,POS Terminal Touch Screen,Mini Capacitive Touch Screen
ShenZhen GreenTouch Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.bbstouch.com
