Industrial Internet of things is the concept of industrial equipment and IT convergence proposed by General Electric (GE) in the fall of 2012. The goal is to use high-performance equipment, low-cost sensors, the Internet, big data collection and analysis technology, etc. The combination significantly increases the efficiency of existing industries and creates new industries.

The wave of industrial internet of things
Now, the wave of industrial IoT led by veteran technology giants GE, IBM and Cisco is changing the industry with large assets.
With connected devices such as Nest and Sonos entering the mainstream, the Internet of Things has become one of the hottest technology trends in the past 20 years, and technology applications in this area have become a hot topic in the application field.
According to CB Insight, IoT startups have attracted a total of $7.4 billion in venture capital over the past six years.

Not only in the development of home and consumer equipment, industries with large assets such as manufacturing, logistics, mining, oil, utilities and agriculture have begun to use IoT systems.
As IoT devices and dedicated sensors collect data at every stage of production, they can help industrial users around the world capture information from their own industrial assets to optimize work efficiency and save money.
Transforming the heavy asset industry
The current wave of industrial Internet of Things is led by traditional technology industry companies such as GE, IBM and Cisco. The Industrial Internet of Things will be the core business of these companies in the future.
In particular, GE, who pioneered the so-called "Industrial Internet" as early as 2012, announced that it would invest $1.5 billion in research and development funds.
GE not only developed the Predix platform for the industrial Internet, but also announced a partnership with Microsoft Cloud to accelerate the digital transformation of industrial users.
Maybe you were an industrial company before falling asleep last night, and today you wake up to become a software and data analysis company.
-- GE Global Chairman Immelt
In recent years, more and more startups have begun to develop sensors, cloud platforms, network infrastructure equipment and machine learning software to extract unknown information from massive amounts of data, which has greatly impacted industrial demand.
Nine leading industries
According to the Industrial IoT startups organized by CB Insights in recent years, we can conclude that the Industrial Internet of Things affects the asset-focused industries mainly in nine areas.
1 Manufacturing and supply chain industry:
Such companies are using connected devices to enhance the ability to collect data during manufacturing and supply chain processes.
These companies include CargoSense, which produces sensors for connecting to keep a close eye on moving products.
In addition to tracking temperature, humidity, pressure and luminosity, the sensors monitor vibration and tilt and record how the goods are handled on the pallet or container.
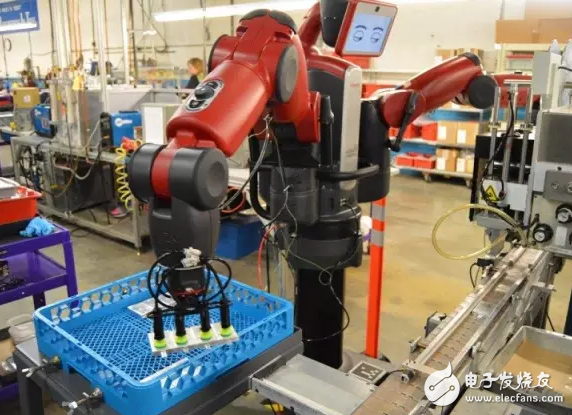

In addition, companies that produce robots, such as Momentum Machines and Rethink RoboTIcs, produce collaborative robots for manufacturing, and RoboCV, which manufactures robots for warehousing.
2 Extractive industries and heavy industry:
These companies are primarily companies that design sensor platforms that are used in industries such as oil, gas, mining and construction that require helmets.
There are also startups that are developing in specific vertical areas, such as companies that build sensor networks for oil and gas companies, such as Groundsensing (focusing on the exploration business), Tachyus (focusing on refining the oil and gas business) and Aptomar (focus on Leakage business) and so on.

There is also Skycatch, which uses drones to collect data for 3D rendering on construction sites.
3 industrial grade wearable technology:
Industrial IoT applications are an important topic for the development of wearable technology in the enterprise market and will become an indispensable tool for inspection in factory automation.
Some companies have already started in this area, for example: Human CondiTIon Safety has established a platform that combines wearable technology, artificial intelligence and building information modeling (BIM) technology to provide security for workers in the manufacturing, energy, warehousing, construction and other industries. .
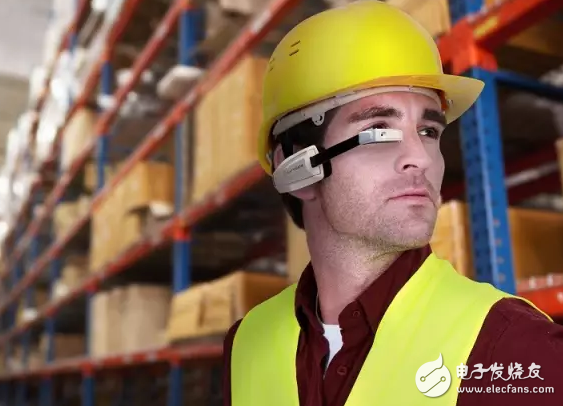

XOEye Technologies provides collaborative work and communication solutions for manufacturing, construction and other industries through wearable hardware and software platforms to increase productivity.
4 Network Infrastructure and Sensor Developers:
Such companies are building networks and developing physical sensors that will lay the foundation for the development of industrial IoT as a whole.
For example, Samsara and DorsaVi are developing industrial-grade sensors that can be applied to a variety of applications, including applications in freight management, machine equipment, energy and industrial-grade wearables.
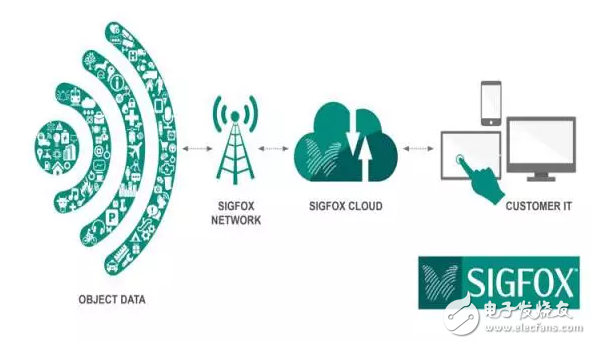
Other companies such as SigFox have built wireless networks for industrial IoT, low-cost, low-cost wireless networks, connected to meters, smart watches or washing machines, and the infrastructure provided to make the so-called Internet of Things a reality.
These keywords represent critical components and applications within the electrical and industrial sector. Here's how they can be classified:
-
Frequency Converter: A frequency converter is a device that converts the frequency of an alternating current (AC) to match the requirement of a particular electrical device or system. This allows equipment designed for specific frequency to operate in regions where the electrical supply has a different frequency. For example, a frequency converter can be used to allow a device designed for a 60Hz supply to operate in a region with a 50Hz supply.
-
Variable Frequency Drive (VFD): A VFD is a type of motor controller that drives an electric motor by varying the frequency and voltage of its power supply. VFDs have significant applications in industrial systems and machinery, where they allow for precise control of motor speed and torque, leading to increased efficiency and longevity of equipment.
-
Pumps, Fans, Conveyors: These are common applications of motors controlled by VFDs. The variable speed provided by the VFD allows these systems to operate more efficiently and adjust to the specific demands of their task. For instance, a pump's flow can be controlled more accurately, fans can be speed adjusted according to the cooling requirement, and conveyor speed can be precisely managed based on the production line's needs.
-
Phase Motor: A phase motor refers to the type of electric motor, which operates based on the phase of the power supply. The most common types are single-phase motors and three-phase motors. Single-phase motors are usually found in lower power applications like household appliances, while three-phase motors are used in higher power applications, often in industrial settings. These motors can be controlled using VFDs for enhanced performance and efficiency.
These components play significant roles in various industries and are essential for efficient operation in many modern systems. The use of VFDs and phase motors, in particular, has revolutionized the way we control and optimize industrial processes, leading to substantial improvements in energy efficiency and system longevity.


Frequency Converter,Variable Frequency Drive,Pumps Fans Conveyors,Phase Motor
WuXi Spread Electrical Co.,LTD , https://www.vfdspread.com
