As mentioned in the previous article, the application of dual cameras is mainly divided into: distance-related applications, optical zoom, dark light compensation, and 3D shooting and modeling. The principle of each application is somewhat different, we will introduce the related principles separately:
Distance related applications
The human eye can easily locate the distance of an object, but when one closes one of his eyes, the positioning ability will drop a lot.
Dual cameras are applications that simulate the human eye.
To put it simply, when measuring the distance, it is calculated by the algorithm. The angles θ1 and θ2 of the subject and the left / right camera, plus a fixed y value (that is, the center distance of the two cameras), it is very easy to calculate the z value (That is, the distance from the object to the Camera)
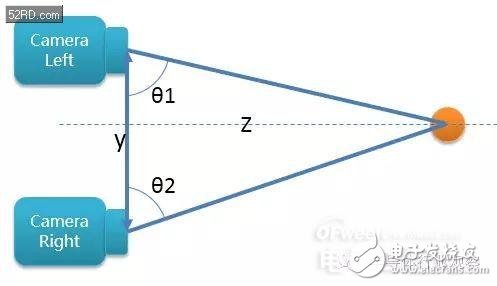
However, this is also easy to calculate. If the center distance between the two cameras is too small, the calculable object distance will be very close. If you want to calculate a long distance, you must make the left and right cameras farther apart.
optical zoom
Optical zoom mainly uses different FOV (angle of view) for the left and right cameras, so that the two cameras have different views. When the user needs a wide-angle photo, the left camera with a viewing angle of 85 degrees is used for framing to obtain a wide-angle effect. When the user needs a telephoto photo, the right camera with a viewing angle of 45 degrees is used for framing to obtain a telephoto effect.
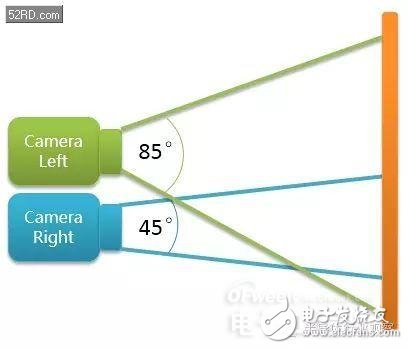
In order to make the objects captured by the left and right cameras have a high degree of overlap, the dual camera module with optical zoom cannot be as wide as the camera module used for applications, but the left and right cameras need to be placed as close as possible.
Dark light enhancement
In fact, in the second part, the editor has briefly introduced the principle of dark light enhancement. Generally speaking, to do dark light enhancement is to use two cameras, one RGBG standard camera, and one black and white camera with RGBG filter removed. RGBG is used to obtain the color of the object, and the black and white camera is used to obtain a better amount of light to judge the light intensity of the object being photographed. Then merge the two pictures to get better dark light enhancement.
But generally speaking, there are two fusion methods:
1. Take the black and white picture as the main body, paste the color of each pixel obtained from the color picture onto the black and white picture, and fuse the two pictures.
2. Using color pictures as the main body, the brightness intensity of each image obtained on the black and white pictures is compensated to the color photos, and the two pictures are merged.
As for which method is more suitable for integration, it is possible that the benevolent sees the benevolent and the wise sees the wisdom.
In the same way, for dark light enhancement, in order to make the objects shot by the left and right cameras overlap the height of the image, such dual camera modules are also required to be as close as possible.
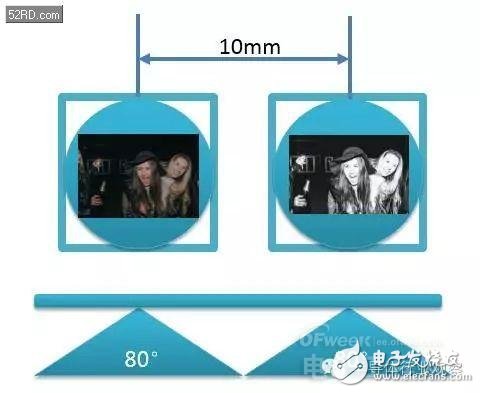
What needs to be explained, Huawei P9 actually chooses the module in this way.
Of course, some people in the industry also said that the effect of this algorithm is not obvious. Dark light compensation is really helpful for users, especially when shooting night scenes. However, some customers think that the Dual PD technology of Sony and Samsung is very good, and they are more willing to use the Dual PD camera for dark light compensation.
Whether the dual camera or Dual PD's dark light compensation effect is good, you can compare the Huawei P9 and Samsung's Galaxy S7 edge, there will be an answer.
3D shooting and 3D modeling
The algorithm of 3D shooting and 3D modeling is actually a bit similar to the application of distance, except that its accuracy requirements are higher, and sometimes infrared distance measurement is sometimes needed for more accurate distance judgment. The editor will not introduce it in detail here.
Requirements for ISP
When it comes to the dual-camera algorithm, I have to mention ISP (Image Signal Processing). The main function of ISP is to post-process the signal output by the front-end image sensor. The main functions are linear correction, noise removal, and dead point removal. Interpolation, white balance, automatic exposure control, etc., rely on ISP to restore the site details under different optical conditions. ISP technology determines the imaging quality of mobile phones to a large extent.
In the functional machine era, ISPs are built on cameras, and cameras with different pixels are equipped with ISPs with different performances. As the pixels of mobile phone cameras are getting higher and higher, the requirements for ISP performance are getting higher and higher. If the ISP is integrated into the camera Sensor, it will inevitably cause the camera module to be too large, and even affect the photo effect. So in the era of smart phones, ISPs are generally on the main chip SoC. In order to achieve better results, some brand customers even add an ISP at any cost to achieve better and more professional photo effects.
A good camera algorithm needs to be paired with a good ISP, and the ISP and algorithm complement each other and are indispensable. The dual camera requires more ISP performance. First, in order to enable the signals of the left and right cameras to be processed at the same time, a single ISP has been unable to meet the needs of dual cameras. This requires a dual-channel ISP to achieve this function.
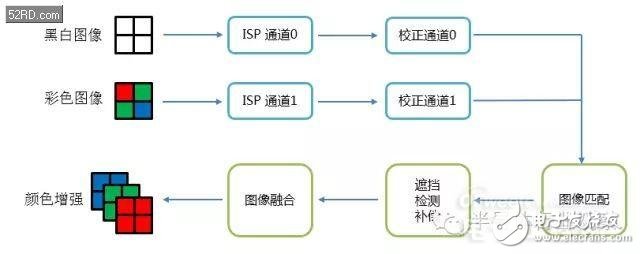
Taking dark light enhancement as an example, the color / black and white images enter the respective ISP channel and calibration channel respectively, and then match the two pictures (such as extracting the same part of the two pictures, removing the part captured by only one camera), Then through occlusion, detection, compensation and other algorithms to process related pictures. Finally, the two pictures are fused together to achieve color enhancement. Of course, in fact, the ISP cooperates with the algorithm to do much more than what is written in this picture. I really do n’t know, so I ’m not misleading everyone.
Of course, there is also a small episode in it. After all, it is two ISPs. The two ISPs have some problems in processing speed and processing capacity. In order to ensure that the two ISPs can sample at the same time, the pictures taken by the dual cameras need to be taken at the same time. One solution is to make the Sensor have a synchronization signal pin. The synchronization signals of the two cameras are docked, and each time the picture is read, the picture is stamped with a time stamp. The ISP passes the time stamp to ensure that the photos taken by the left and right cameras are taken at the same time, and finally merged.
Camera interface
Generally speaking, the camera interfaces of current smart phones are MIPI interfaces. Previous mobile phone platforms only had 2 MIPI interfaces, which were respectively for the front camera and the rear camera. Doing dual cameras requires the platform to support at least three MIPI interfaces. In fact, on the previous high-end platforms, in order to achieve higher pixels, dual-channel ISPs have been used (for example, to support 16M cameras, 2-channel 8M-capable ISPs will be used). Such platforms are likely to have only two MIPI. But this can't stop the engineer from doing the front single camera + rear dual camera.
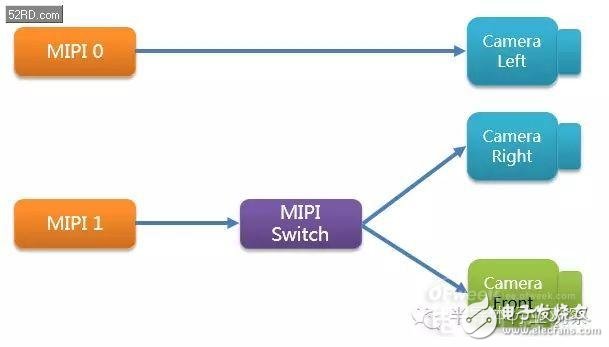
That's right, with a small SwTIch, you can easily achieve dual cameras.
Used in electronic products, Computers ,mobile phone
Dongguan Bofan technology Co., LTD , https://www.pengliandz.com
