introduction
This article refers to the address: http://
With the rapid spread of mobile phones, the uplink and downlink data rates supported by wireless networks continue to increase, and new applications, especially data services, are emerging, and mobile phones have become indispensable information terminals around people. More and more people use mobile phones instead of watches, notepads, MP3s. Will one day our wallets and keys will be given to mobile phones, making our lives more convenient and safer? Near Field Communication (NFC) technology will make this a reality. In June 2006, Nokia and China Mobile, Philips, and E-Tongka launched the first NFC mobile payment test in China in Xiamen. Users can use the Nokia 3220 mobile phone with embedded NFC module to make mobile payment at any business outlet (bus, ferry, cinema, fast food restaurant) covered by Yitong Card in Xiamen. Not only that, but in the near future, through the combination of mobile phones and NFC technology, users can realize the following applications only by using mobile phones: downloading concert time and place schedules on street posters and magazines; playing interactive orientation in the park. Off-road game; refresh the arrival time of the bus in the station in real time; send SMS in the office to control the time when the housekeeping staff enters and leave the house; replace the existing student ID card and student card in the school; check the map and bus in the smart public phone booth all over the city Information such as lines, food and beverages; payment at any gas station, supermarket, bank where there is a POS machine and receiving electronic invoices with mobile phones.
1 Technical introduction
NFC is a new technology based on the integration of radio frequency identification (RFID) and interconnection technologies. It is a short-range wireless communication technology standard. It integrates a contactless card reader, a contactless smart card and a point-to-point function on a single chip. It operates in the frequency range of 13.56MHz and can establish a connection between devices in a range of approximately 10cm. The transmission rate can be 106kbit. /s, 212kbit/s, 424 kbit/s, can be increased to 848kbit/s or more in the future. NFC terminals have three modes of operation:
(1) In the active mode, the NFC terminal acts as a card reader and actively sends out its own RF field to identify and read/write other NFC devices;
(2) In passive mode, the NFC terminal can simulate a card being read/written, which only passively responds in the RF field emitted by other devices;
(3) In the two-way mode, both parties actively send out the RF field to establish peer-to-peer communication.
NFC is used to quickly establish wireless communication between various devices over a short distance. It can be used as a virtual connector to exchange data between any two wireless devices. It also enables devices to communicate over longer distances or transmit data at higher rates by initializing the device's native Bluetooth and 802.11 wireless protocols. Therefore, in addition to information transmission, NFC devices can serve as a secure gateway in the connected world, allowing users to store or receive various information at any time, whether at home or on the move. As long as the two NFC devices are brought together, they will automatically start the network communication function, and the user does not need to set the installation program separately, thereby implementing the aforementioned electronic wallet and identity card functions such as contactless mobile payment and identification. NFC technology conforms to the ISO18092 and ISO21481 standards of the International Organization for Standardization, and is compatible with the wireless smart card ISO14443 standard, and complies with the European Computer Society's EMCA-340, 352 and 356 standards. The two strongest NFC-compatible contactless smart cards -- Philips' MIFARE technology and Sony's FeliCa technology -- have deployed about 1.2 billion smart cards based on the former, and the latter has deployed about 170 million. This makes NFC technology fully capable of low-power, low-cost, and compatible features of future short-range wireless interconnection equipment, making NFC a highly competitive technology in the field of short-range wireless interconnection.
2 Application classification and status
2.1 Application Classification The application of NFC technology can be divided into five categories:
(1) Touch and Go, such as access control, tickets and tickets, users can store the ticket or gated device close to the card reader, and can also be used for logistics management.
(2) Touch and Pay, such as contactless mobile payment, the user can pay the device close to the POS machine embedded with the NFC module and confirm the transaction.
(3) Touch and Connect, such as connecting two NFC devices (such as mobile phones and laptops in Figure 1), performing peer-to-peer data transmission, such as downloading music, transferring pictures and Exchange contacts and so on.

Figure 1 NFC point-to-point communication for mobile phones and laptops
(4) Touch and Explore, users can connect NFC mobile phones to NFC-enabled smart public phones or posters to browse traffic information.
(5) Download and Touch, the user can receive or download information through the GPRS network for payment or access control functions. As mentioned above, the user can send a text message of a specific format to the mobile phone of the housekeeping attendant to control the housekeeping attendant to enter and leave the house. permission.
2.2 Status of application at home and abroad
The NFC Forum, a non-profit industry association founded by Nokia, Philips and Sony in 2004, currently has 11 sponsored members, including Samsung, Microsoft, Visa, etc., and its total number of members has exceeded 100. Leading operators, handset manufacturers, chip vendors, smart card manufacturers, banks and credit card organizations (see Table 1).
Table 1 Global NFC mobile phone test project
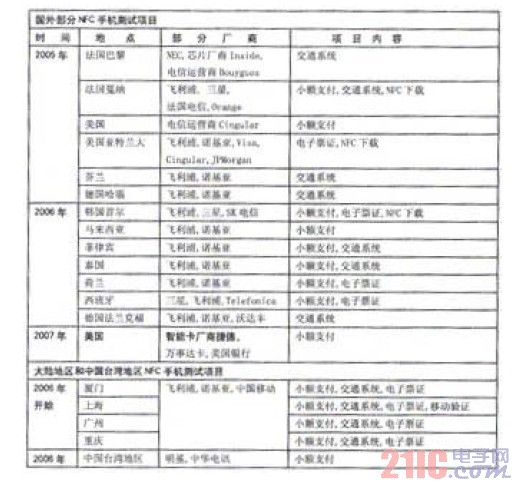
In Japan, since NTT DoCoMo launched its mobile phone wallet business based on Felica technology in July 2004, its user base has been described as “hugeâ€, and POS machines supporting Felica have been seen everywhere on the streets of Japan. After several upgrades, Felica phones have been widely used in transactions, identification, access control and other aspects. The huge transaction volume prompted NTT DoCoMo to establish a financial services division through the acquisition of a 34% stake in Sumitomo Mitsui Credit Card Corporation. In Hong Kong, China, Felica technology is used on the Octopus card with e-wallet and identification capabilities, and the card has been released in the tens of millions. Felica technology is also widely used in Singapore. In the European Union, the StoLPaN (Store Logistics and Payment with NFC) project, which is jointly invested by the European Commission and the Information Society Technology (IST) project, and by companies such as Motorola and the University of Budapest, is also scheduled to be released in the summer of 2007. Version of technical specifications and applications, and demonstrates the use of NFC in transportation and closed payment systems. The project aims to develop an open commercial and technical architecture for NFC-based services, driving the deployment of NFC-based mobile applications across a wide range of industries.
3 Comparison with other wireless communication technologies
NFC is derived from RFID technology but is different from RFID. NFC uses two-way identification and connection. There is no fixed master-slave relationship between the parties. Communication can be initiated by any NFC device. Infrared communication requires the device to be within 30° cone angle and cannot move. As a consumer-oriented payment technology, NFC is faster than infrared and easier to operate. Compared with Bluetooth, NFC is suitable for close-range transactions and is suitable for exchanging important information such as financial information or sensitive personal information. Bluetooth is suitable for long-distance data communication and can make up for the shortage of NFC communication distance. NFC and Bluetooth can complement each other and coexist. Simultaneously,
The very close communication distance also gives NFC a natural security guarantee. ZigBee is better suited for industrial control applications with a large number of wireless sensors and control operations, while Wi-Fi is clearly better suited for small office spaces and home networks (see Table 2).
Table 2 Comparison of NFC and six wireless communication technologies
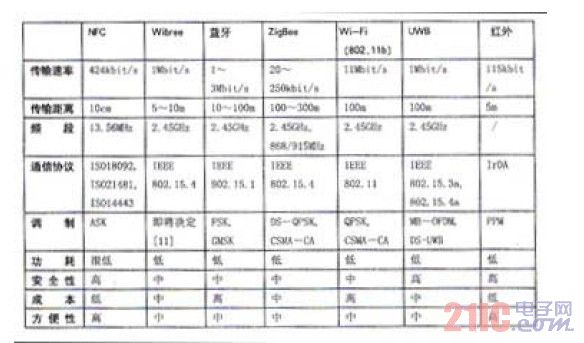
In terms of cost, the cost of NFC is low, and Philips promises that the cost per chip is about $2. The system cost of Bluetooth, Wi-Fi and ZigBee is much higher than that of NFC. In general, as a wireless communication technology for close-range transactions, NFC has obvious advantages, low power consumption, low cost, and good security. Its rate can basically meet the information exchange requirements between devices. At the same time, for applications such as video streams that require higher bandwidth, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi and other technologies can also be used to provide convenient automatic access.
4 Several applications for contactless mobile payment
At present, mobile phone-based contactless mobile payment applications have three mainstream solutions: mobile phone-based NFC solutions proposed by Philips, Sony and Nokia, and eNFC solutions and dual-interface smart card solutions proposed by chip maker Inside.
4.1 Mainstream solutions
(1) NFC solution
In this solution, the NFC function chip and antenna are independent of other parts of the mobile phone and the SIM card, but the NFC module shares the battery with the mobile phone (see Figure 3). When the battery is powered, the NFC module can work in active, passive and bidirectional modes; when the battery is powered off, it can only work in passive mode, which is equivalent to an ordinary card. The mobile phone switch has no effect on the NFC module, that is, the NFC function can also be used when the phone is turned off. There are two ways to achieve this: one is to customize the mobile phone, integrate the antenna on the mobile phone battery or the motherboard, so that the NFC application and the mobile phone are integrated, the work is stable and reliable, but the mobile phone needs to be replaced; the second is to connect the antenna directly to the NFC chip, and then The battery is placed close to the battery and the back cover of the mobile phone. The user does not need to change the mobile phone. The aforementioned Xiamen test project adopts this method, as shown in Figure 2. The shortcoming of this solution is that the reliability of the antenna connection is not high; in addition, there are special requirements for the internal size of the mobile phone, and the increase of the antenna affects the portability of the mobile phone. The NFC module of this solution cannot communicate with the processor or SIM card of the mobile phone, and the user and the telecom operator cannot control the NFC module through the mobile phone. This will result in separate contact between the credit card issuer and the handset manufacturer, completely out of the market structure of the telecom operator. On the other hand, if you want to link the information sent and received by the NFC module to the cellular network, you must establish an interface between the NFC module and the mobile phone baseband chip, and the design of each layer must bypass the operator's control, and can not directly read and write SIM. Cards, hardware and software design will become very complicated. The advantage of this solution is that it has good card compatibility for different technologies and different credit card issuers. There are many cases in the world, and the application technology is relatively mature, which is more suitable for the pilot project.

Figure 2 Nokia 3220 in the Xiamen test
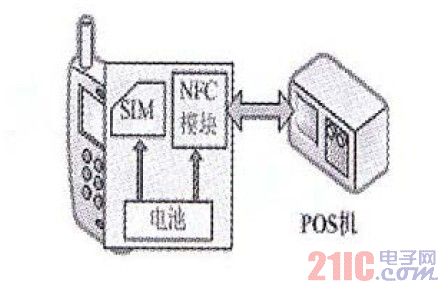
Figure 3 Schematic diagram of the NFC scheme
(2) eNFC solution
This solution, also known as the convergence scheme of mobile phone and SIM card, separates the application layer and the underlying functions, puts the NFC application in the SIM card, and puts the NFC function chip in the mobile phone (as shown in Figure 4) to solve the compatibility problem. Due to the large capacity of the SIM card, important information (such as credit card account number and employee card number) can be stored in the SIM card, and the security of the SIM card storage is higher, and only one pin is added to the SIM card. When the user replaces the SIM card, the existing transaction data can be taken away to achieve complete machine card separation. This solution simplifies the communication structure between the NFC module and the mobile phone, makes the NFC network application smoother, and enables telecom operators and credit card issuers to join the market. The disadvantage is that high-speed transmission between the NFC module and the SIM card is required to ensure real-time performance and fast operation, but this communication protocol has not been standardized yet. The French Paris transport system in Table 1 uses this approach.
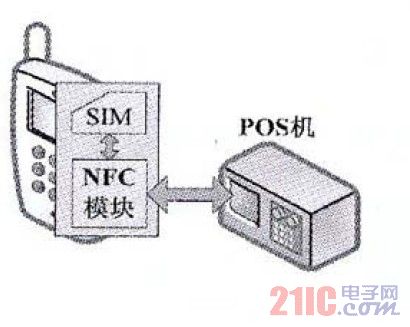
Figure 4 Schematic diagram of the eNFC solution
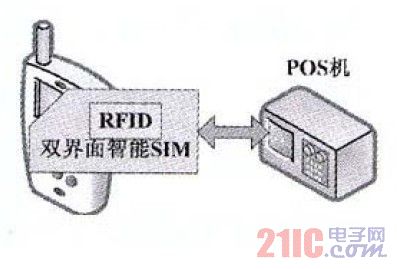
Figure 5 Schematic diagram of dual interface smart card solution
(3) Dual interface smart card solution
The solution is based on a dual-interface smart SIM card that supports contactless applications and also implements the functions of an ordinary mobile phone SIM card. It does not affect contactless operation when answering calls and sending and receiving text messages (see Figure 5). The two implementations are basically the same as the NFC solution: one is to customize the mobile phone; the other is to directly connect the antenna to the SIM card and place it between the battery and the back cover of the mobile phone, so that only the SIM card can be replaced, and the cost is reduced. Low reliability and high requirements for mobile phone size. The solution occupies the C4 and C8 interfaces, which are used for high-speed data downloads and may affect future high-speed over-the-air applications. This solution is based on smart card technology, and technical standards and specifications have been formed; for operators, the project starts faster and costs are lower. Since the SIM card can only be issued by the operator, the solution is more advantageous to the operator. Currently, Hunan Mobile is conducting internal testing of the program.
4.2 Transition plan
In addition, given that the current non-contact mobile payment is still in its infancy, it will take some time for the standard to be unified and the user to accept the service. Therefore, two transitional solutions are worth considering:
(1) RFID module + independent RFID card
In this solution, the RFID card is a single card that is independent of the mobile phone, and is the same as the existing RFID cards, and does not need to be replaced. The RFID module is a dedicated RFID read/write module built into the mobile phone. As shown in Figure 6, it is the same as the NFC solution. The shared battery and antenna are built in and cannot communicate with the SIM card of the mobile phone. The independent RFID card can be used like a normal card, and can also accept the operation of the read/write module. The main function of the read/write module is to check the balance on the card, and the future can be extended to the recharge operation. The advantage of this solution is that the independent RFID card makes the existing card readers in buses, shops and the like basically need not be replaced, and the simplified dedicated reading and writing module also makes the system cost lower. The shortcoming is that the function of the reading and writing module is limited, and the network application is extremely complicated as with the NFC solution; and the user needs to carry the mobile phone and the RFID card when consuming.
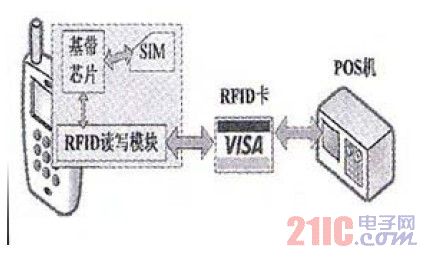
Figure 6 Schematic diagram of RFID module + independent RFID card
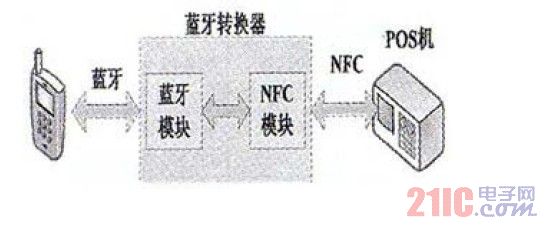
Figure 7 Bluetooth + NFC schematic
(2) Bluetooth + NFC
The core of the solution is a Bluetooth converter, which contains Bluetooth and NFC modules. The modules can be connected by RS232 interface. When in use, the mobile phone first connects to the converter through Bluetooth, and the converter internally converts the message format to the NFC module, and then the NFC module connects with the NFC-enabled POS machine, as shown in FIG. 7. This solution is suitable for most mobile phones with Bluetooth without NFC function. The converter can be integrated into the POS so that Bluetooth or NFC-enabled mobile phones can pay and do not carry cards. Due to the relatively high cost of the Bluetooth module, it is also integrated with the NFC module, which increases the cost of the POS machine and is not conducive to widespread deployment; the communication between the Bluetooth communication and the converter module is also lower than that of the NFC mode.
5 problems
The most important and complex issue surrounding the commercial deployment of NFC applications is to create an NFC ecosystem in which all parties can share benefits, the most subtle of which is the relationship between telecom operators and credit card issuers. On the one hand, operators and distributors can contact the equipment vendors alone to form an exclusive NFC service network, which is used in the market; on the other hand, operators and distribution
The cooperation of the business can expand the business and attract more users. The case of NTT DoCoMo's injection of Sumitomo Mitsui Credit Card Company has shown the trend of cooperation in the two major industries in Japan. In China, operators' independent network construction will be restricted by financial business access; publishers can build networks separately and cannot use telecommunication networks, and services are greatly limited. The cooperation between the two sides has the influence of market leading power, regulatory control, control over users, the depth of penetration and penetration of the telecommunications industry and the financial industry. These are all to be solved by further development of technology and market. The NFC-enabled mobile phone is more secure, and the user can turn on the payment function by using the password when using it, and close it in time after the end of use. Once the phone is lost, as long as the password is set, others will not be able to use it. Users can also set different passwords for various functions such as access control, but users should also prevent people from peeking into passwords when they consume.
In addition, there are some issues that are worth noting.
5.1 Reporting loss
Since it takes more time to enter a password, especially when it is frequently used, most users do not set multiple passwords for the phone, such as boot, SMS, Internet, and long distance calls. Therefore, the user will not set up multiple passwords such as consumption and access control for the NFC mobile phone because of trouble, which causes the operator to report the loss of the mobile phone when the mobile phone is lost. However, when the mobile phone is powered off or shut down, the operator cannot report the loss through the mobile network. At this time, the mobile phone also has the functions of consumption and access control in the NFC passive mode, which requires reporting the loss of the NFC module of the mobile phone in the wired POS network. , causing the POS machine to reject its service request. The question that arises is whether the access control of the home or office also needs to access the wired network. If it is not connected, how to identify that the mobile phone has been lost; if access, how to prevent the attacker from illegally controlling the access control through the wired network. Even if the user sets a password for the access control, it is also difficult to open the door when the mobile phone is turned off or powered off.
5.2 Viruses and Trojans
Today, mobile phones are smart, users can install a variety of software for mobile phones, and can also install third-party developed software to extend NFC applications. And these software, even SMS or WAP pages may be hidden from viruses and Trojans. How to prevent personal information and funds in mobile phones from being stolen by illegal programs, or NFC functions being controlled by illegal programs is an issue that needs further study.
5.3 Illegal POS machine
How to prevent an attacker from using an illegal POS machine with a camouflage or a poster embedded with a chip, etc., also needs to be studied for illegal reading and writing operations on the mobile phone.
5.4 Virtual currency
When mobile payment is popularized, it will no longer be limited to “small amountâ€. Users will greatly rely on virtual currency (electronic money) from the withdrawal of wages to various consumption, and the amount of physical money circulating in the market will be greatly reduced. . How government departments conduct effective policy and legal supervision of these electronic transactions and virtual currencies is also an issue to be further studied.
6 Conclusion
With the popularity of mobile phones and the launch of new mobile services in the 3G era, contactless mobile payments will become a trend. Under this trend, the various stakeholders formed around the industrial chain will gradually form a balanced ecosystem under the joint efforts of technology and market. In the long run, contactless mobile payment technology must support smooth web applications and peer-to-peer communications, and almost all technologies will now transition in this direction.
LiFePO4 Lithium Wall Mounted Battery
RIMA LFP Series power wall LiFePO4 batteries are an ideal choice for both home energy storage systems and small-medium enterprises (SMEs). Our highly qualified research and development team has designed these batteries with an ultra-modern design, ensuring an exceptionally long service life and unparalleled reliability in energy storage.
One of the key technical features of our batteries is their excellent performance in higher temperatures. They are designed to withstand and perform optimally even in extreme temperature conditions, making them suitable for various environments. Additionally, our LiFePO4 batteries offer a higher capacity range, allowing for more energy storage and longer usage times.
Another advantage of our LiFePO4 batteries is their lighter weight compared to traditional battery options. This makes them easier to handle and install, without compromising on their storage capacity or performance. Moreover, these batteries operate in a pollution-free manner, contributing to a cleaner and greener environment.
Due to these technical advantages, our LiFePO4 batteries have gained significant popularity among users and have experienced rapid development. They have become the preferred choice for those seeking high-quality energy storage battery solutions that meet their demanding requirements.
In conclusion, RIMA LFP Series power wall LiFePO4 batteries offer exceptional performance, reliability, and longevity in energy storage. With their advanced features, including excellent performance in higher temperatures, higher capacity range, lighter weight, and pollution-free operation, these batteries have become the go-to solution for those who require top-notch energy storage capabilities.
Solar Lithium Batteries,LiFePO4 Lithium Batteries,Wall Mounted Battery
OREMA POWER CO., LTD. , https://www.oremabattery.com
