The gray scale is the brightness resolution of each LED on the display. For example, 4bit gray scale means that the LED has 16 levels of brightness changes. The gray scale control of the LED driver chip is implemented as shown in Figure 1. The gray scale of LED brightness is controlled by the OE width and SDI on the driver chip. Take the gray scale 5 to be displayed by the first LED in Figure 1 as an example, SDI must turn on the output switch when the OE width is 1 and 4 , In order to get the overall LED display gray scale is 5. The gray scale is 9, 4, and 11 and so on. Different SDI and OE width permutations are combined to get different LED gray scales, which will also show different LED brightness changes. In addition, the shorter the unit width of the OE, the shorter the cycle for completing a grayscale change, that is, the higher the refresh rate that can be obtained per unit time.

The shortest pulse width and response time (tr/tf) of the OE in the driver chip determine the level of gray scale. The so-called shortest OE pulse width is the effective width that the OE can be turned on under the condition that the linearity of the output current of all channels can be maintained. The smaller the OE pulse width, the higher the output color gradation, that is, the faster the output current response, the higher the refresh rate and output gray gradation. Among them, the refresh rate and output gray scale are related to the shortest pulse width of OE, system data transmission speed, and the number of serially connected chips are related to the number of chip output channels. As shown in Figure 2, the reference formula is listed as follows:

Frefresh: refresh rate (Hz)
According to the above reference formula, if a single controller has 8 output ports, with a cross-sectional area of ​​64×64 monochrome screen, the number of serially connected chips required is NIC=32, and the output gray scale is set to 12 bits (4,096 levels) ), if you use a driver chip with 16 output channels, a data transmission speed of 20MHz and a shortest OE pulse width of 300ns, you can get a refresh rate of 723Hz by substituting into the calculation, but if you want to increase the output gray scale to 14 bits (4,096 levels) , The refresh rate is reduced to 196Hz, if the output grayscale is to be increased to 16-bit (65,536 levels), the refresh rate is only 50Hz, and the general system input screen update rate is at least 60Hz, so such a low refresh rate is no longer possible Supply the needs of general display system.

In the above situation, if you want to increase the output gray scale and at the same time want to increase the refresh rate, you can choose a driver chip with a smaller OE pulse width. If a chip with the shortest OE pulse width of 50ns is used, even if the data transmission speed is 10MHz, the output gray scale is increased to 16 bits (65,536 levels), the refresh rate can still output 287Hz, and the output gray scale is set to 14 bits (4,096 levels). ), the refresh rate can be increased to 1001Hz, and when the output grayscale is set back to 12-bit (4,096 levels), the refresh rate can be greatly increased to 1,953Hz. Therefore, the smaller the OE pulse width, the higher the output color gradation and the refresh rate of the screen, the higher the output color gradation provides more colorful LED display images, and the high refresh rate provides smooth and flicker-free images on the LED display. Play.
The influence of the shortest OE pulse width on the output current surge

Figure 3 The output current waveform with a larger 0E pulse width
The size of the OE pulse width is a key factor affecting the output current surge. As shown in Figure 3, when the OE pulse width is greater than 500ns, the rise time of the output current is 37.99ns, and no surge is generated. However, if you want to get a higher output color level and a faster picture refresh rate, you must reduce the OE pulse width, but a smaller OE pulse width requires a faster rise/fall time (tr/tf) to maintain the integrity of the pulse width However, the faster tr/tf will cause the output current of the general LED driver chip to produce a surge. As shown in Figure 4, when the OE pulse width is less than 100ns, the rise time of the output current is 8.2ns. According to Faraday’s law, VL= L(dI/dt), it can be clearly seen that the output current produces a serious surge phenomenon when the output current is turned off, and the output current surge may not only break down the output channel of the driver chip, cause chip damage, but also make the entire LED The phenomenon of electromagnetic wave interference of the display screen becomes serious, and the display screen will shake or even damage the system.
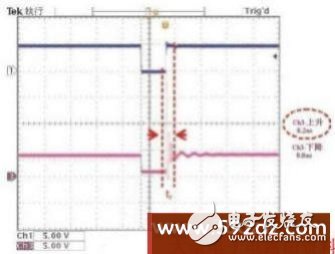
Figure 4 Small OE pulse width produces severe spikes
Improvement of current surgeTo improve the above-mentioned LED driver chip output current surge, you can reduce the switching speed of the output channel, and stagger the switching time between the output channels. The so-called switching speed of the output channel is to control the slew-rate of the output channel. The longer the rise/fall time (tr/tf) of the output current, the smoother the waveform of the output current rise/fall, and the more the current surge can be suppressed. The phenomenon of waves reduces electromagnetic interference. But too much tr/tf will produce distorted waveforms, which will affect the response speed of the output current. Therefore, the LED driver chip must be able to achieve the best balance between the switching speed of the output channel tr/tf and the current surge.
In addition, staggering the switching time between the output channels can also improve the output current surge of the LED driver chip, that is, reducing the instantaneous current of the power supply line by not turning on and off the output channels at the same instant. As shown in Figure 5, the four output channels OUT0~OUT3 on the left are turned on at the same instant, resulting in a large inrush current. On the other hand, the four channels on the right have staggered outputs, and the instantaneous current of the power supply is averaged. Disperse, reduce the peak current, and also improve the output current surge and electromagnetic interference. Figure 6 shows the actual measurement of the Macroblock LED driver chip. The switching time waveform diagram between the output channels is staggered. The two adjacent channels have a delay time of approximately 15ns.
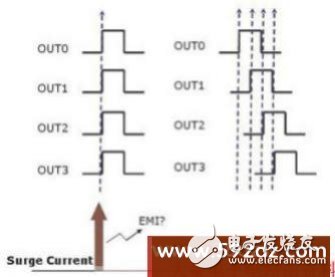
Figure 5 Stagger the switching time between output channels
To meet the demand for high-end display screens, in addition to having a high refresh rate to enable the LED display to play images smoothly and without flicker, it also needs the ability to have high output color levels to achieve more colorful LED display images. The above two requirements can be improved by selecting LED drivers with shorter OE pulse width to increase the refresh rate and output color level, but the use of external gray scale control will still be affected by the system transmission speed and bandwidth limitations, and reduce the refresh rate And output color scale. Another option is to use a built-in PWM control LED driver chip, which can increase the transmission speed with a smaller amount of data transmission, and achieve the effect of improving the refresh rate and output color level. For the LED driver with shorter OE pulse width, please refer to Macroblock's MBI5036, and for the built-in PWM control LED driver chip, refer to Macroblock's MBI5042. (Photoelectric News Network Lin Xinhong)
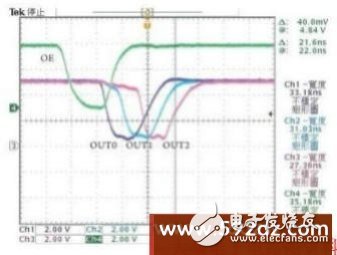
Figure 6 *Waveform diagram of the switching time between the staggered output channels actually measured by the LED driver chip
21Kw Ac Charging Pile,Wall-Mounted Ac Charging Pile,Portable Ac Charging Pile,New National Standard Fast Charging Pile
Guangdong ChongWei Technology Ltd. , https://www.chongweitech.com
