1. What are the negative effects of lighting on the living environment?
Whether the living environment is natural, ecological and green has become a concern of the world today. The living environment is inseparable from the light environment, but whether the light environment is suitable for people, whether the atmospheric environment, the animal and plant ecological environment associated with the light environment are destroyed, and whether it ultimately affects human beings is the reality we have to face.
Since the artificial lighting, he has brought light, vitality, joy and modern civilization to mankind. At the same time, however, artificial lighting does not bring about all positive effects. He will inevitably have some negative impact on the living environment. In particular, excessive artificial lighting, for animals, plants, buildings, etc., may have a negative effect on the environment in which human beings depend for themselves, such as growth patterns, physiology and chemistry, and physical chemistry.
The concrete manifestations are: excessive artificial lighting wastes electric energy and aggravates air pollution; the brightness of the night sky background is obviously improved, affecting people's normal life and scientific research activities; destroying the judgment of animals and plants on the alternating changes of the natural environment, disrupting its growth law; Light pollution affects people's physical and mental health; affects buildings through photochemical effects.
2. What is light pollution?
Light pollution generally refers to various kinds of light that affect the natural environment, adversely affect human normal life, work, rest and entertainment, damage people's ability to observe objects, cause uncomfortable feelings and damage human health.
Optical radiation from wavelengths of 10 nm to 1 mm, that is, ultraviolet radiation, visible light, and infrared radiation, may become sources of light pollution under different conditions. The various light pollution generated by artificial lighting will have a negative impact on astronomical observation, human health, transportation, animal and plant growth and ecological environment.
3. What are the common types of light pollution?
(1) According to the international law
1) Artificial daylight. Refers to outdoor lighting at night, shopping malls, neon lights upstairs in the hotel, light box advertising and lighting signs and site lighting. It has a serious impact on people's normal work and rest, disrupting the body's biological clock, resulting in low efficiency during daytime work. Artificial daylight can also damage birds and insects, and glare can destroy the normal reproduction of insects at night.
2) White and bright pollution. It refers to the reflection of the glass curtain wall, glazed brick wall, polished marble and various paints of the buildings in the city during the daytime when the sun is shining brightly, which is bright and bright, dazzling and dazzling. It may become the culprit in the manufacture of traffic accidents, and it will have a negative effect on nearby residential buildings. Reflected light can increase the indoor temperature, and household appliances and furniture are prone to aging, which may cause fires.
3) Color light pollution. Refers to the light pollution caused by black light, rotating light and fluorescent light in the dance hall, which is the most harmful to the human body in light pollution. The most common black light in the ballroom produces high levels of UV light and has a long lasting effect on the human body. If the human body receives this kind of radiation for a long time, it can induce nosebleeds, tooth loss, cataracts, and even leukemia and other cancers.
(2) According to the type of light pollution
1) Glare. It is the visual condition in the field of view due to the unfavorable release or range of brightness, or extreme brightness contrast in space or time, resulting in discomfort and reduced visibility of the object.
2) Interfering with light. The amount of astigmatism, direction or spectrum of light that causes discomfort, distraction, or loss of visual information in a particular situation.
3) Spilled light. Light that scatters from the illumination device and illuminates outside the illumination range.
4) Reflected light. The light from outdoor lighting passes through walls, floors or other illuminated surfaces that reflect the surrounding space and interfere with people and the environment.
5) Sky glow. Night sky light from the scattering of gas molecules and aerosols from the atmosphere, including visible and non-visible light. It consists of two separate components: natural sky glow and artificial sky glow.
4. Have you been disturbed by glare?
Glare is the most important form of light pollution in cities. When there are high-intensity objects in the field of view that are larger than the brightness level that the eye can adapt, or objects with extremely high brightness, there will be troubles, discomfort, and reduced visibility. Physically and psychologically interfered or even hurt. We know that there are two types of discomfort glare and disability glare according to their degree of influence.
When encountering uncomfortable glare, as the name suggests, the human eye will feel uncomfortable. The physiological cause of this discomfort is mainly due to the stimulation of high-intensity light, which causes the pupil to shrink, or the light scattering in the intraocular tissue such as the cornea and the lens to form a light curtain in the eye, or because the retina is stimulated by high brightness. But despite being uncomfortable, it does not necessarily reduce the visibility of the visual object. For example, the interior of a house, classroom, office, or furniture material is very bright, the light is shining on it, and the mirror reflection is made to make the eyes uncomfortable. At night, it is time to fall asleep, but the light outside the window of the room is very bright. People can't sleep; the lights installed in the classroom don't have enough shading angles. Just look up the teacher and see a row of light-emitting tubes that are neither comfortable nor distracting. These uncomfortable glare interferences are almost met by everyone.
If you encounter disability glare, it will reduce the visibility of the visual object, which will reduce people's visual function. For example, if the steel-making workers do not have the glasses in front of the blast furnace, the newly-released molten iron will burn the eyes of the people; some street lamps have no light-cutting measures, and the glare of the street lamps makes the eyes of the drivers and pedestrians unable to see the direction; some drivers When driving at night, the headlights are turned on for a long time. The pedestrians across the road can't see anything at all. The eyes must go through some effort to gradually see the objects. This is the interference of disability glare. In particular, the LED flashlight has high brightness and strong directivity. Such flashlight should not directly illuminate the human face; the laser pointer is very clear on the projection screen, but it cannot be illuminated to the human eye. Stab, reducing or even losing visual function.
In short, we must take measures to limit glare pollution, build a harmonious light environment, and avoid glare interference as much as possible.
5. Why are the stars and the Milky Way in the sky in some cities invisible?
The dark blue night sky and the stars are twinkling, so the natural and beautiful night sky has become a childhood memory for most people in the city. Nowadays, children living in the city are rare to see the starry night sky and the beautiful Milky Way. In addition to air pollution, there is an important reason for the excessive artificial light entering the sky, which increases the brightness of the city's night sky, thus reducing the visibility of the night sky. The bright sky casts a layer of tulle on the eyes, leading to visual shielding, which reduces the ability of astronomers and astronomers to observe stars and other celestial bodies. Therefore, people have become accustomed to not looking at the sky at night, and the effect of skylight on astronomical observations is shown in the figure.
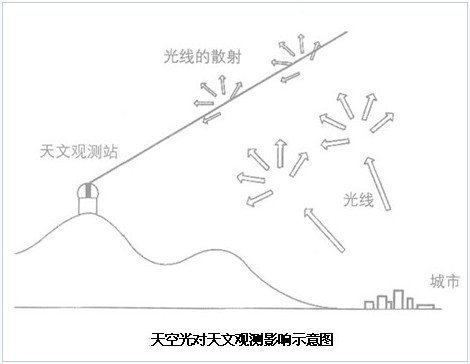
At present, two-thirds of the world's population has no visibility of the Milky Way, and now most cities can only see less than 200 stars. Light pollution has caused night cities to hang under the glowing sky, and people gradually lose their true nights. Although humans have made considerable efforts to control light pollution, in the past few years, the sky glow is still expanding globally. Although it is difficult to quantitatively predict how much it will increase each year, studies have shown that the night sky brightness growth rate will not be low. At 3%, if you increase at this rate, the brightness of the night sky will double after 23 years.
6. What are the characteristics of light pollution?
Light pollution has the following characteristics:
1) Light pollution violations are perceptible in terms of individual behavior. As long as the light pollution exists, it will be displayed from the beginning. If the light is reflected, the reflected light enters the car at high speed, which will cause sudden temporary blindness or visual illusion, and will cover the motor vehicle driving in an instant. The visibility of the staff, or making them feel dizzy, seriously endangers the safety of pedestrians and motor vehicle drivers, but this does not have to wait for how long it takes to reach the infringement.
2) Light pollution is simple in the judgment of the subject. For example, under the reflection of strong light, people can find the source of pollution by following the direction of light.
3) Light pollution violations have intermittent and time-space uncertainties. The strong light is reflected as an angle of light, and as long as the angle is different, the corresponding infringement also changes.
4) Compared with other environmental pollution, light pollution is difficult to eliminate or mitigate by means of decomposition, transformation and dilution. Therefore, prevention and control should be based on prevention.
7. How to suppress light pollution?
The main measures to suppress light pollution are:
1) Avoid unnecessary and excessive lighting. The International Commission on Illumination has published a number of documents covering roads, various sports venues (soccer, tennis, swimming, ice sports, etc.), advertising and other lighting standards. Combined with China's national conditions, China's national standards include "Architectural Lighting Design Standards". The industry standards include "Urban Road Lighting Design Standards" and "Urban Night Lighting Design Specifications". Indoor and outdoor lighting construction should implement standards, and should not be arbitrary, and break through the standards.
2) Use qualified lighting equipment. That is, using lighting equipment that can avoid or reduce light pollution. The luminaire should not emit light in the sky, the brightness is appropriate, only the area or object that needs to be illuminated, the place where it is not needed to be illuminated, and the object passively received light, that is, the spilled light is prevented. The spilled light projected outside the object should not exceed 25% of the total light output of the luminaire. At the same time, some places can use high-efficiency and narrow-band light sources (such as low-pressure sodium lamps), and their optical radiation can be filtered out by filters without affecting astronomical observations outside their range.
3) Select the appropriate lighting method and take the necessary lighting control. This control includes space control and time cavity. Strong string lamps and laser lamps such as searchlights and narrow beam floodlights should be strictly restricted to the sky and crowds.
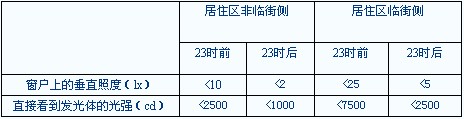
Residential, apartment, hospital ward building, etc. should not be equipped with night lighting; the night lighting facilities should be strictly controlled for the interference of residential, apartment, hospital ward, etc., the maximum vertical illumination on the windows of the residential room and hospital ward and the direct view from the room The maximum intensity of the illuminant should not be greater than the values ​​specified in the table below.
Interference light control on the windows of residential and hospital wards
When setting up night lighting, try to avoid interference with the normal growth of animals and plants. Rare trees should not be equipped with night lighting. The glass curtain wall of a building should not be floodlit.
8. What kind of light environment is suitable for animal life?
Animals and humans glimpse, relying on the sun to proliferate. Natural light affects the survival, activity and distribution of animals. Light is also the main information that organisms use to detect seasonal changes in the environment and produce corresponding responses. The evolution of thousands of years has made animals extremely accurate to the light of the sun, the moon and the stars at night. The change of day and night, the intensity of sunlight, has a decisive control effect on the animal's work, growth and ecological characteristics.
According to the different responses of animals to light, animals can be divided into four ecological types: limp animals (hi light animals), nocturnal animals (hidden animals), morning faint animals and full day and night animals.
1) Liming animals. Daytime activities, rest at night, can adapt to higher light intensity. Such as most birds, primates in mammals, ungulates, chinchillas, marmots, squirrels, reptile lizards and insects such as butterflies, mites, flies and so on.
2) Nocturnal animals. Adapt to weaker light levels, nighttime activities, and rest during the day. Such as night monkeys, brown rat, squirrels and other beasts, nightingales, night hawks, nightingales, etc. in birds; reptile geckos, as well as amphibians, mites, insects and night moths. It should be pointed out that nocturnal animals require relatively weak light intensity, and the weaker the light intensity, the better. The weak light will affect the normal life of such animals.
3) Morning faint animals. Refers to animals that like to move in the light of the night before dawn or dawn. Such as some bats, hedgehogs, etc.
4) Full day and night animals. It refers to animals that can move 24 hours a day, and can adapt to both strong light and low light. Such as voles, sable, tussah and so on.
All day and night activities and Minhang animals can withstand changes in the light quality of the factory, belonging to the broad-light group. Nocturnal and faint animals can only adapt to changes in light quality in a relatively narrow range, belonging to the narrow-light group. Soil organisms and endoparasites are almost always protected from light.
9. Why do fly traps can trap mosquitoes and flies, while mosquito repellent lights keep mosquitoes away?
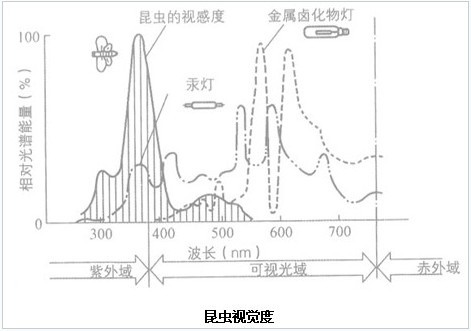
Different light sources have different degrees of preference for insects. This phenomenon is determined by insects' different judgments on light quality such as different light colors and spectra.
Insects, like humans, can distinguish between different colors, but at a different wavelength than humans. Insects can perceive wavelengths ranging from 240 nm (ultraviolet light) to 700 nm (yellow, orange). Studies have shown that manta rays have the best visual sense of color, followed by butterflies and moths. Bees cannot distinguish between orange red and green, and ramie butterflies do not see green and yellow green. Flies and mosquitoes can also see the color. House flies hate blue most, so they don't want to be close to blue doors and windows and mosquito nets. Mosquitoes can distinguish between yellow, blue and black, and prefer black and hate yellow. Generally insects cannot feel red.
  Different shades and brightness, the degree of attraction to insects is also different, l 000cd / m2 light is the induction zone of insect phototaxis, and mosquitoes are most active in 1lx illumination environment.
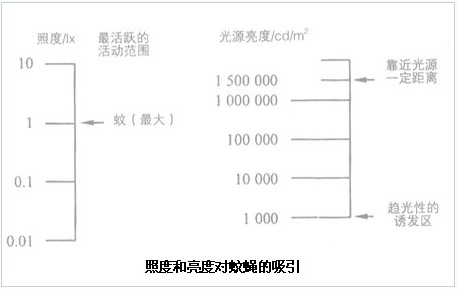
According to the insect's preference for different light colors and different illuminance (brightness) light, people can create some special lamps. For example, a flytrap lamp is a luminaire that uses near-ultraviolet light in a light source to induce mosquitoes to touch the grid or drown. The mosquito repellent lamp is a kind of lamp developed by utilizing the characteristics that the mosquito is disgusting to the yellow spectrum.
10. How does the light of the night city affect the animals?
All the creatures on the earth have evolved in the natural laws of day and night. The emergence of the “Never Night City†has greatly disturbed the animal's ecological characteristics for natural light for thousands of years. It disturbs the natural laws of animal growth, breeding and activities, leading to serious ecological consequences of the series.
Studies have shown that except for a very small number of animals that are active at night, most animals are quiet at night and do not like strong light. However, the sky light, the spill light, the interference light and the reflected light generated by the night city illumination often brighten the animal life and the rest environment, disrupting the rhythm of the animal's day and night biological clock, making it impossible to fall asleep and rest, and even affect eating. , reproduction and survival. If the animal absorbs the radiant energy of the illumination, it not only causes changes in body temperature, but also changes in the life of the animal. When the goldfish is placed in a magnetic field, the stronger the magnetic field strength, the more the fish do not want to eat the bait. Under the sudden illumination of artificial light, the frog will stop eating, mating, and even staying there for a long time after the light is extinguished. The salamander, in the glory of yellow and red, loses its ability to discern direction and cannot climb from one pond to another. Animals that live entirely in the water are no better than amphibians and terrestrial animals in a lightly polluted environment. Scientists have carefully observed small vertebrates living in the water. The results show that the amount of nocturnal activity decreases in proportion to the time they receive exposure, and the number of algae that they prey on the surface is also decreasing, which causes algae to flourish. The water quality deteriorates, which is more detrimental to the survival of aquatic animals.
Lights can also seriously mislead animals. For example, newly hatched turtles usually swim into the water according to the reflection of the moon and stars in the water, but the lights on the shore exceed the brightness of the moon stars, causing the newly born turtles to misplace the land. When the ocean is alive and thirsty.
Light is the deadly killer of insects. A small advertising light box can kill hundreds of thousands of insects a year. The reduction of insects threatens the pollination of plants and the food source of birds, affecting the survival of a series of animals and plants. The lights of "Never Night City" can be transmitted far away, so that some animals far away from the light source are also stimulated, unable to sleep at night, consuming energy for foraging, self-defense, and reproduction, and dying. There was a group of cranes flying over the city for a night because of the over-lighting of a city's lighting. Finally, they were exhausted and fell to the ground, killing more than 100 people. According to American ornithologists, 4 million migratory birds slammed into the high-rise advertising lights every year and died. A tall building in a city killed 1,500 migratory birds every year. They all mistakenly used the lights of tall buildings as victims of the stars.
Like air pollution, water pollution, etc., light pollution can harm animal species in the city and its surrounding areas. Just considering the bright night illumination not only harms people's health, but also increasingly threatens the survival of animals.
There are many ways to prevent animals from being exposed to artificial light. Reasonable nighttime lighting, scientific light source selection, proper lighting time, etc., can minimize the threat of artificial light to the survival of animals, ensuring that animals will not die out due to artificial light stimulation.
11. In what ways can night lighting reduce the impact on animals?
Many studies have shown that not all artificial light can cause harm to a certain species. Suitable light source selection, scientific lighting methods, and appropriate lighting time can greatly reduce the impact of nighttime animals on artificial lighting.
Some studies have found that when the artificial illumination time lasts for 4 hours, the number of deaths of surrounding small flying insects increases sharply. When the illumination time is less than 2 hours, the impact is small, which makes the small flying insects have the opportunity of self-recovery and regulation.
Metal halide lamps are more attractive to cockroaches, cockroaches and small flying insects than high-pressure sodium lamps of the same brightness.
The photoperiod response of insects has a certain choice of light wave properties. The most sensitive light is generally blue-violet light (350-510 nm).
Through the study of the ecosystem, we will find environmentally friendly green lighting that does not affect the lighting effect of the night scene and maintains the stable development of the ecosystem.
12. What is the role of light in plant growth?
Light is the source of energy for photosynthesis, and plants convert sunlight into energy that can be utilized by other forms of life in the biosphere through photosynthesis. The light energy used by plants in photosynthesis is mainly concentrated in the red and blue regions of terrestrial plants, while the submersed plants in aquatic plants mainly use light with shorter wavelengths, such as marine algae, which can utilize green light.
Only the visible portion of solar radiation can be utilized by photosynthesis. Solar radiation that can be utilized by photosynthesis is called physiologically active radiation, and is physiologically and ecologically understood as photosynthetically active radiation, which accounts for about 40% to 50% of solar radiation. In physiologically effective radiation, the order of validity of each spectrum is red orange light > blue purple light > yellow light > green light. Green light is rarely used in the photosynthesis of terrestrial plants, called physiologically non-active radiation.
The process by which plants rely on light for growth, development, and differentiation is called photomorphogenesis. Photosynthesis is a high-energy reaction (which requires intense illumination) that converts light energy into chemical energy. The light form is a low-energy reaction (no need for too strong light), and light acts only as a signal to excite the photoreceptor, pushing a series of reactions in the cell, and finally showing a change in morphological structure. The energy of the red light required for light morphogenesis and the general photosynthesis light compensation point (the plant's photosynthetic intensity and respiratory intensity reach equal illuminance values) differ by 10 orders of magnitude, which is very weak. Red light and far red light can determine the change of light form, and the light body is phytochrome, which can control plant seed germination, organ differentiation, growth and movement, photoperiod and flower induction. Appropriate light energy promotes cell division and elongation, tissue and organ differentiation, and increases growth rate.
13. What is the photoperiod of plants?
The length of sunshine is the most rigorous and stable cyclical change on Earth, so plants are used as the most reliable information for developmental and behavioral rhythms. Plants distributed in various parts of the Earth have long adapted to the specific pattern of day and night length changes, forming an annual cycle of reproduction and behavior initiated by a specific day, that is, the photoperiod of plants.
The ecological effects of sunshine length on plants mainly include light information and total energy. The effect of changes in the length of sunlight on plants can be analyzed from the response of plants to day length. The photoperiod is actually an adaptation strategy of plants, which is conducive to making full use of resources and avoiding unfavorable seasons. It has been determined that the photoperiod of most plants is not caused by the length of the sun, but by the length of the continuous darkness. The minimum or maximum dark length that causes plant reproduction (flower bud formation) is called critical night length. The deciduous dormancy, leaf emergence, and underground storage organ formation of plants also respond to the length of sunshine.
14. Does lighting affect plant growth?
Plant growth is inseparable from light, which in turn affects plant growth. Natural light, whether it is intensity or time, has formed a pattern of plant adaptation, and this adaptation has been completed after a long period of biological evolution. If you artificially change some factor in this balance, it will Break this kind of squat, thus affecting and even threatening plants. The time of illumination, spectral distribution, and light intensity all affect plant growth in all aspects.
Both the light in artificial lighting and the sunlight in nature affect the growth of plants in the form of light energy. Therefore, whether it is natural light or artificial light, the effect on plants is the same, that is, the energy dynamics of photosynthesis and the signal of light form. The difference is that natural light has strict natural laws, and plants have adapted to and formed the corresponding living structure and system, just as humans adapt to the law of survival during the daytime work and rest at night. Artificial light, such as disturbing the nighttime environment in the living environment of plants, causes plants to make false judgments and change normal growth patterns, thereby forming damage to plant survival.
15. What effect does the brightness of light have on plants?
The brightness of light is a physical quantity that is subjective to human perception. For plants, it should be said that the light intensity. In general, Xiguang plants are more adaptable to light intensity than hi-yin plants. For hi-light plants, sufficient light is a necessary condition for normal growth. Excessive light can cause burns and even life-threatening. Excessive light will hinder its normal growth and development. The yin plants also have a range of light intensity suitable for their growth, and the light intensity is too high or too low.
The adaptation types of plants adapted to light intensity can be mainly divided into three categories:
1) Positive plants. It can grow and develop vigorously in a strong light environment, and grows poorly under low light. The pioneer plants of the community belong to this category.
2) Negative plants. Under low light, it grows better than strong light, and strong light is affected. For example, many species of yin ferns and orchids are in the bottom layer.
3) Shale-tolerant plants. It has two meanings: it grows best under full sunlight, and can endure certain shaded plant groups; the second is a group that needs moderately weak light at some stage of life history (mainly seedling stage). For example, Cyclobalanopsis glauca and Pinus koraiensis are not tolerant to glare at the seedling stage, so they live under the shadow of the upper trees, and when they reach adulthood, they reach the upper layer of the canopy and become positive plants.
In fact, the above plants adapt to the change of light quality while adapting to strong light. Under low light, the spectral composition is significantly different from that of full sunlight. The light components suitable for photosynthesis under the forest are gradually absorbed and reduced from top to bottom, and the green light is mainly near the ground.
16. What are the effects of light color on plants?
The physical quantity reflected by the color of light is the wavelength of light, and light of different wavelengths will show different colors of light. Higher plants have extremely fine light receiving systems and signal transmission systems. In addition to containing a large amount of pigments, higher plants also contain trace pigments, which can sense light information, such as the direction of light, duration of light, light intensity, spectrum, etc., thereby amplifying the signal, which means that the object can follow the external light. Respond accordingly to changes in the environment. The effect of light on growth and development is achieved by blue to ultraviolet radiation and red to near infrared radiation. At least three types of photoreceptors are known to be involved in photoregulation reactions in higher plants, such as phytochromes, flowering pigments or blue/ultraviolet-A receptors and ultraviolet-B receptors.
In physiologically effective radiation, violet and cyan light inhibit elongation and affect phototropism; blue light causes chloroplast movement; red light promotes elongation growth; ultraviolet light is inhibited by plant growth hormone to inhibit stem elongation and promote anthocyanin Formed and caused to the light, such as the flowers on the mountains, and more rosettes. Infrared light promotes the prolongation of plant stems, and infrared rays promote seed and spore germination and increase plant body temperature. UV-B radiation can damage the genetic material DNA of terrestrial higher plants, affecting and inhibiting photosynthesis.
17. What is the effect of light exposure time on plants?
The effect of light exposure time on plants can be analyzed from two perspectives:
1) Absolute time, that is, when to illuminate. Most of the artificial lighting is started at night, but like humans, plants need a dark rest environment at night. Inappropriate artificial lighting can disrupt the photoperiod of plants and affect their growth and development.
2) Relative time, that is, how long, the daytime illumination is a natural phenomenon and has long been adapted to plants, and long-time artificial lighting at night will disrupt the normal growth cycle of plants and may even endanger life. For example, some plants complete the induction of flowers after a certain period of low temperature treatment, and in some plants, he requires changes in the length of day and night. Usually for spring flowering plants, the sunshine must be long enough (the darkness is short enough). For autumn flowering plants, the sunshine must be short enough (the darkness is long enough).
18. Why can't you throw away discarded fluorescent tubes?
A fluorescent lamp is a low-pressure mercury discharge lamp filled with argon or other inert gas and a small amount of mercury. Mercury is a white liquid metal at room temperature with a specific gravity of 13.5, a freezing point of -38.89 ° C and a boiling point of 357.25 ° C. Among all metals, mercury has the lowest melting point and boiling point. Mercury evaporates at room temperature, producing mercury vapor. The amount of mercury evaporated depends on the size and temperature of the evaporation surface area. The larger the surface area, the higher the temperature, and the greater the amount of evaporation. Mercury is often present in the air as a vapor that invades the body through the respiratory tract, skin and digestive tract. The toxicity of mercury has an accumulating effect. Under normal circumstances, mostly chronic poisoning, it affects the nerve central system, and can also cause gingivitis, diarrhea, ambiguity and trembling. If the discarded lamp is broken, the mercury in the tube will be completely dispersed, which will become a long-term source of mercury vapor, which will cause serious pollution. So we can't litter the discarded fluorescent tubes.
19. Does artificial lighting cause damage to ancient buildings?
After thousands of years of practical experience, our ancient construction workers invented the beautifully-arched arches, which supported the larger eaves as a load-bearing structure. In order to protect the wooden structure of the arch and beautify the building, it is decorated with paint. Most of these paints are hidden under the roof of a building and are not easily exposed to direct sunlight. The materials used in color painting have limited ability to withstand light. Some of the traditional organic materials can not be kept in direct sunlight for several years. If the night lighting is applied to ancient buildings, the night arch paintings will show rich structure and color under the illumination of lights. However, direct exposure to high temperature and high light will accelerate the shortening of the life of the color painting, resulting in fading and discoloration. It has been verified by experiments that infrared light and ultraviolet rays are the most important influences on the oil painting color in the illumination source.
1) Infrared: In the long-term illumination of the heat radiation source, the oil color painting layer and the inner wood material layer produce temperature changes. The more severe the temperature change, the greater the temperature stress, the stronger the thermal expansion and contraction effect, and the softening of the color paint. And so on. The landscape lighting of ancient buildings allows the wooden members to receive artificial illumination every day for a fixed period of time, thus constituting a cyclical change in surface and internal temperature stress. These action processes on the interior of the wood base layer may cause the wood mechanism to be loosely deformed (small), thereby reducing the bearing capacity and service life of the member; for the oil painting color layer, cracking, violent skin, and shedding may occur.
2) Ultraviolet light: The energy of ultraviolet light is 314-419kJ/mol (kJ/mol), and the activation energy of most polymer auto-oxidation reaction is about 42-167kJ/mol, and the dissociation energy of various chemical bonds is about 167~ 418kJ/mol. Therefore, the energy of ultraviolet light is enough to destroy the chemical bond of the polymer, and the aging degradation by the photochemical oxidation reaction destroys the oil painting of the ancient building skin. Therefore, the oil painting and color painting should be treated with UV protection.
LED outdoor wall lights are widely used in residential areas, tourist attractions, squares, parks, private gardens, courtyard corridors and other public places to illuminate. It not only effectively provides people with travel safety, but also has an important role in the construction of the entire comfortable environment. Function, during the day LED Outdoor wall lamp can embellish the city scenery, at night LED outdoor wall lamp can not only provide the necessary lighting, but also increase the residents' sense of security to interpret the bright style
 Our other products range:LED Underground Light, LED Underwater Light , LED Wall Washer Light, LED Linear Light , LED Outdoor Flood Light, LED Garden Light , LED Landscape Light , LED Strip Light , Led Step Light etc.
Our other products range:LED Underground Light, LED Underwater Light , LED Wall Washer Light, LED Linear Light , LED Outdoor Flood Light, LED Garden Light , LED Landscape Light , LED Strip Light , Led Step Light etc.
IP67 Outdoor Wall light,IP67 Wall light,waterproof wall light,Wall lamp waterproof.Outdoor wall mounted light
SHENGYA LIGHTING TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD. , https://www.syalighting.com
