Development and application of video communication technology
1 Introduction
With the development of modern communication technology and services, people's demand for communication has changed from the initial single voice demand to the communication demand for video and audio. The video communication service that integrates voice, data, and video has become a development in the communication field Hotspots, with point-to-point or multi-point video and audio communication as the main form of video conferencing, telemedicine, and distance education, are increasingly used.
2. The development status of video communication technology
(1) Bearer network
Video communication services can be carried on the underlying networks of different technologies, from the early public telephone network, to narrow-band ISDN, DDN, ATM and now widely used IP networks can become the bearer network of video communication services. Due to the real-time nature of video communication and the characteristics of image transmission, the bearer network is required to have sufficient bandwidth, short delay, and low bit error rate.
Public telephone network. Narrowband ISDN and DDN are circuit-switched networks. Circuit-switched networks are connection-oriented networks with stable transmission rates and delays, small end-to-end delays, and low bit error rates. Therefore, video communication quality is easily guaranteed. But its shortcoming is that the connection is fixed. In addition to dialing on the public telephone network and the ISDN network, other network applications must have a point-to-point permanent connection. The bandwidth utilization rate is low, the openness is very poor, and it is not convenient to set up the connection. The H.320 standard is the first video communication framework protocol developed by ITU-T in 1990 to meet and adapt to this type of circuit-switched network. The earliest commercial video communication system was built on this basis. In the public telephone network, the voice band data is used to transfer video information. The standard followed is the H.324 series launched by ITU-T since 1995. It is currently mainly used in videophone services.
ATM performs information transmission by means of fast packet switching and statistical time division multiplexing. Due to its complex technology, expensive equipment, and the slow development of ATM standards, it has not been applied on a large scale. At present, it is impossible for ATM networks to achieve end-to-end applications. Instead, it has become a transmission platform that supports multiple applications. . The ITU-T H.321 standard and H.310 standard are exactly the video communication standards and specifications for the ATM network structure.
In recent years, the IP of communication networks has become the mainstream of network development, and video communication based on IP networks has been widely used and widely developed. The IP network is a connection-free network using the TCP / IP protocol. The H.323 standard is a video communication standard developed by the ITU-T in 1996 and applied to the IP network. It is called "multimedia audio-visual on a local area network that does not guarantee service quality." System ", and expanded to" packet-based multimedia communication system "in 1998, namely ITU-TH.323v2, and later launched H.323v3 and H.323v4 versions, it is currently a video communication standard with a large number of commercial users , And has been widely valued by countries around the world.
(2) Framework agreement for video communication
With the continuous development of communication network technology, the bearer network of the video communication system has evolved from a circuit-switched network to a flexible and highly scalable IP network. Therefore, the frame protocol of video communication has produced H.320, H.324, H.310 and H.323 four standards, the current H.323-based video communication system applications dominate the market.
H.320 is a series of standards with a transmission rate between 64kbit / s-2Mbit / s. Its main component provides H.221 with a standard for multiplexing audio, video, data and control information into a single bitstream. Time division multiplexing (TDM) system, frame length is 10ms. H.230 / H.242 provides standards for mode commands and instructions and function exchange. H.261 provides standards for video coding. H.263 is a new optional method that can provide better image quality. G.721 provides standards for audio coding. G.722 and G.728 are optional alternatives. In addition to video and audio channels, data can be transferred when needed. For example, T.120 meeting.
The H.324-based videophone system runs on the public telephone network (PSTN) with a transmission rate of 28.8-64 kbit / s, which can provide real-time communication of voice, image, and other data. H.324 is a series of protocols, including V.34 modem protocol, H.223 data multiplexing and branching protocol, H.245 system control protocol, G.723.1 voice algorithm, H.261 and H.263 image algorithm.
The H.323 standard covers the communication of audio, video, and data on IP packet-based networks (LAN, EXTRANET, and Internet). The layered structure of the H.323V2 standard mainly includes: H.225.O standard packet and Synchronization, H.26l and H.263 standard video codec, G.711, G.722, G.728, G.723 and other standard audio codec, and related communication control protocol H.245, etc. In addition, T The .120 standard adds and expands the functions of data conferencing for H.323 terminals, such as multi-point electronic whiteboard (T.126), multi-point file transfer (T.127), multi-point application sharing (T.128), etc. Data conference function.
(3) Video communication codec technology
Video and audio codec technology is a key technology in video communication. In 1988, ITU-T promulgated the draft recommendation H.261, which proposed hybrid coding as the core, and later formulated a series of video coding standards, such as MPEG-1 of H.262.H.263.ISO of ITU-T, MPEG-2 etc.
H.261 is the earliest moving image compression standard, which was developed by ITU-T for IS-DN to carry out videophone and video conference, and the rate is an integer multiple of 64kbit / s. It specifies the various parts of video coding, including motion-compensated inter prediction, DCT transform, quantization, entropy coding, and rate control that adapts to fixed-rate channels. H.261 only processes CIF and QCIF image formats. Each frame of image is divided into image layer, macro block group (GOB) layer, macro block (MB) layer, and block (Block) layer for processing.
H.263 is a draft standard of ITU-T, designed for low-stream video coding. The second edition (H.263 +) and H.263 ++ that appeared later added many options to make it more widely applicable. Compared with H.261, the coding algorithm of H.263 has made some improvements and changes to improve performance and error correction capability. H.263 + introduced by IUT-T in 1998 is the second version of H.263 recommendation. It provides 12 new negotiable modes and other features, which further improves the performance of compression coding. In addition, H.263 + has improved the unrestricted motion vector mode in H.263, plus 12 new optional modes, which not only improve the coding performance, but also enhance the flexibility of application. H.263 has basically replaced H.261. H263 ++ adds three options on the basis of H263 +. These three options are: Option U, Option V and Option W, mainly to enhance the bit error resistance performance of the bitstream on the harsh channel, and at the same time to improve the enhanced coding efficiency.
MPEG is the abbreviation of Moving Picture Exports Group. It was established in 1988. It is an expert group that develops compression standards for digital video / audio. Currently, MPEG-1, MPEG-2, MPEG-4 and other standards have been proposed. The MPEG-1 standard was published in August 1993, and is used to encode 1.5Mbit / s data transmission rate of digital storage media moving images and their accompanying audio encoding. The standard consists of five parts: the first part explains how to encode audio and video in accordance with the provisions of the second part (video) and the third part (audio). The fourth part explains the process of verifying that the output bitstream of the decoder or encoder meets the requirements of the first three parts. The fifth part is an encoder and decoder implemented in complete C language. The MPEG organization launched the MPEG-2 compression standard in 1994 to realize the possibility of interoperability of video / audio services and applications. The MPEG-2 standard is a detailed specification for the compression scheme and system layer of standard digital TV and high-definition TV under various applications. MPEG-2 has made more detailed regulations and further improvements in system and transmission, and is particularly applicable The encoding and transmission of digital TV at the broadcast level is recognized as the encoding standard for SDTV and HDTV. The Moving Picture Experts Group MPEG officially announced the first version of the MPEG-4 (ISO / IEC14496) standard in February 1999. The second version of MPEG-4 was launched at the end of the same year, and officially became an international standard in early 2000. MPEG-4 is very different from MPEG-1 and MPEG-2. MPEG-4 is not just a specific compression algorithm, it is aimed at digital TV, interactive drawing applications (audio and video synthesis content), interactive multimedia (WWW, data extraction International standards developed for integration and compression technology requirements. The MPEG-4 standard integrates numerous multimedia applications into a complete framework, and aims to provide standard algorithms and tools for multimedia communication and application environments.
H.264 / AVC is a new generation of compressed video standards developed by ITU-T's Video Coding Experts Group (VCEG) and ISO / IEC's Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG), which are vigorously developed and researched and adapted to low bit rate transmission. In March 2003, the Joint Video Experts Group (JVT), composed of two expert groups, announced the final draft of this compressed video standard. This standard is called ITU-T H.264 protocol or ISO / IEC MPEG-4 Part of the advanced video encoding. The codec framework of H.264 has no significant changes from previously proposed standards such as H.261, H.263 and MPEG-1 / 2/4, and is also based on a hybrid coding scheme: the entire system is divided into video coding layers and Network abstraction layer. The video coding layer mainly describes the video content carried by the video data to be transmitted. The network abstraction layer considers different applications, such as video conference communication, H.32X continuous packet video transmission or RTP / UDP / IP communication. H.264 not only saves 50% bit rate than H.263 and MPEG-4, but also has better support for network transmission. It introduces an encoding mechanism for IP packets, which is conducive to packet transmission in the network. Streaming media transmission of video in the network. H.264 has strong anti-error characteristics, can adapt to video transmission in wireless channels with high packet loss rate and severe interference, and supports hierarchical coding transmission under different network resources to obtain stable image quality.
3. H.323 video communication architecture based on IP network
According to H.323 recommendations, the IP video communication system consists of terminals, gateways, gatekeepers, IP networks, and multipoint controllers (see Figure 1). The terminal is a client that provides simplex or duplex real-time communication, and needs to support signaling and control functions, codec functions, and so on. The gateway is used to connect with non-H.323 terminals. The gatekeeper performs functions such as address translation, call control and management, bandwidth control and management, and domain management. The multipoint controller is used to support user sessions between three or more points. It consists of a multipoint controller (MC) and a multipoint processor (MP). The MC determines the audio and video processing capabilities of all terminals and controls resources. MP mix , Exchange and process audio, video and data streams. 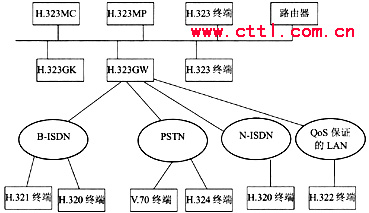
Figure 1 H.323 video communication architecture based on IP network
4. Application status of video communication technology
The outbreak of SARS in 2003 promoted the rapid development of China's video communication industry, and major operators have increased their investment in the construction of video communication networks. At present, China Telecom, China Unicom, China Railcom and China Netcom have all established commercial video communication operation networks. Among them, China Telecom and China Unicom have relatively large networks and have a large number of users.
In 1994, China Telecom built the country's first dedicated conference and party network for conference and television. It adopted a non-standard video network with a point-to-point structure and a relatively small capacity. It did not use a multipoint control device (MCU). This point-to-point network structure is simple, the failure of a single device does not affect other points, and the system has high stability. The disadvantages are high cost and complicated operation. In 1996, the National Public Conference TV Network was built. This network uses a two-level cascade technology with multi-point control equipment, with Beijing MCU as the central point, and one MCU in each of the eight districts as the second-level central point. Each provincial terminal passes a 2M dedicated line circuit Connect to the MCU in this region. With the development of video technology and changes in the communications market, China Telecom has built 2M and 8M high-definition conference television networks for internal use in the group company in 2002 and 2003. 8M high-definition conference television uses MPEG-2 codec technology. In 2002, China Telecom launched the "New Vision" service, which is aimed at low-end users in the market, and the system takes into account the H.320 and H.323 protocols. Support digital leased line, ISDN / LAN / ADSL and many other access methods. Terminals that support access include H.320 terminals, H.323 terminals, and H.320 / H.320 integrated terminals, providing users with comprehensive and diversified services.
China Unicom's "Bao Shi Tong" videoconferencing network is based on China Unicom's data integrated service carrying platform and adopts the H.323 technology system based on IP technology. Users can access this service through a dedicated line or broadband Internet access to Unicom's broadband video network. The whole network adopts multi-level GK networking, with large switching capacity. The whole network supports 15,000 point-to-point video phone calls, supports more than 600 multiparty conferences at the same time, and supports a maximum of 300 parties in a single conference. The entire network video switching equipment (MCU) is mutually Backup.
5. Development prospect of video communication technology
China's video communications industry has been developing for 10 years. In the past, users of video communications were mainly government departments. Until recently, due to the construction and investment of operators' video networks, many enterprise users began to participate. However, issues such as network compatibility and interworking, QoS, and business models have affected the rapid development of video communications. Due to the continuous development of video communication protocols, there are products and networks that support different protocols, and compatibility between these products and networks needs to be resolved. In addition, the functions of video communication equipment still need to be improved. In terms of technical standards and protocols, the H.323 video network based on IP has not done enough to guarantee service quality. Regarding the business model, there is mainly the problem of unclear business models and market positioning, and it is not perfect and flexible in terms of tariffs, billing and settlement.
At present, due to the influence of factors such as the development of the network, the increase of personal income, and the transformation of people's consumption concepts, China has seen a huge demand for video communication services in various industries such as education, medical care, finance, government, and enterprises. With the development of video communication towards openness, integration, popularization, mobility, and personalization, "noble" video communication services will gradually enter the home, and further move toward popularization, making interactive video communication services like surfing the Internet and making phone calls As convenient.
Pink Neon Light,Red Neon Lights,Led Neon Rope Light,Blue Neon Lights
Tes Lighting Co,.Ltd. , https://www.neonflexlight.com
