LLC is an abbreviation for LogicLinkControl, which means: logical link control.
The IEEE established the Local Area Network Standards Committee (IEEE802) in February 1980, specializing in LAN standardization and developing the IEEE 802 standard. The LAN reference model described by the 802 standard only corresponds to the data link layer and the physical layer of the OSI reference model, and it divides the data link layer into a logical link layer LLC sublayer and a medium access control MAC sublayer. The IEEE 802 committee develops a local area network. A series of standards, collectively referred to as the 802 standard. The IEEE802.2LAN standard defines the functions and services of the logical link control LLC sublayer, and is the base standard of IEEE802.3, IEEE802.4 and IEEE802.5.
LLC is responsible for identifying network layer protocols and then encapsulating them. The LLC header tells the data link layer what to do with the packet as soon as it is received. It works like this:
The host receives the frame and looks at its LLC header to find the destination of the packet, for example, the IP protocol at the Internet layer. The LLC sublayer can also provide flow control and control the ordering of the bitstreams.
IEEE802.2LLC is applied to IEEE802.3 (Ethernet) and IEEE802.5 (Token Ring) LANs to achieve the following functions:
1. Manage data link communication
2. Link addressing
3. Define the service access point ServiceAccessPoints (SAP)
4. Sorting
LLC provides a way for the upper layer to handle any type of MAC layer, such as Ethernet IEEE802.3CSMA/CD or Token Ring IEEE 802.5 Token Passing.
LLC was developed on the basis of High-Level Data-Link Control (HDLC) and uses a subset of the HDLC specification. LLC defines three types of data communication operations:
Type 1: No connection. This method does not guarantee that the information sent will be received.
Type 2: Connection oriented. This approach provides four services: connection establishment, acknowledgment and data arrival response, error recovery (implemented by requesting retransmission of received erroneous data), and sliding window (coefficient: 128). A sliding window is used to increase the data transfer rate.
Type 3: Connectionless Response Response Service.
A type 1 LLC connectionless service specifies a static frame format and allows network protocols to run on it. Network type protocols that use the transport layer protocol typically use the service type 1 approach. Type 2 LLC connection-oriented services support reliable data transfer for LAN environments that do not require network layer and transport layer protocols to be invoked.
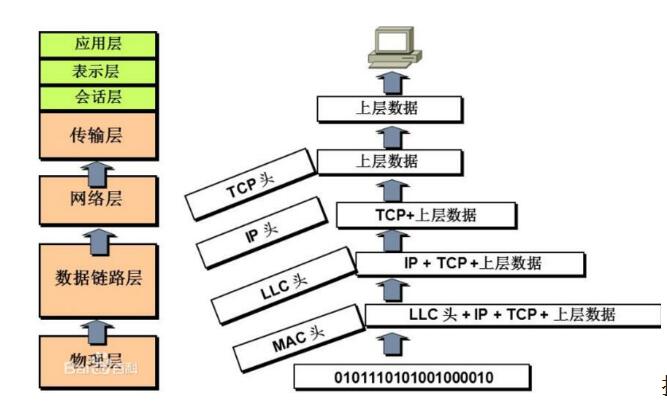
Media access control is to solve the problem of how to allocate the right to use the channel when the use of the shared channel in the local area network competes.
Logical Link LogicalLinks is a protocol-driven communication session between two end systems that exchange communication information on actual or logical circuits. The protocol stack defines the communication of two systems on a medium. A variety of different types of communication protocols are available at the lower level of the protocol stack, such as local area network (LAN), metropolitan area network (MAN), and icon X. 25 or a packet switched network such as Frame Relay. A logical link is formed between two communication systems on a physical link, which can be copper wire, fiber optics, or other medium. According to the OSI protocol model, these logical links exist only above the physical layer. You can think of a logical link as a line that exists between two networked systems in the network.
Connection-oriented services To establish reliable communication, logical lines need to be established, but sessions must be maintained between the two end systems.
A logical line that is transmitted to a service packet that requires an answer connection and that has a return signal. This service creates more overhead but is more reliable.
No answer No connection service does not require answering and pre-delivery. There is no session between the end systems.
The data link layer in the OSI protocol stack can be further subdivided into a lower Medium Access Control (MAC) sublayer and a higher Logical Link Control (LLC) sublayer. When it receives a packet, it passes up from the MAC sublayer. If multiple networks and devices are connected, the LLC layer may send packets to another network. For example, on a NetWare server, you might have both an Ethernet adapter and a Token Network Adapter installed. NetWare automatically bridges between the networks connected to the adapter so that packets originally on the Ethernet can be sent to the token network. The destination, the LLC layer is like the exchange between network segments or link relay, it reassembles the Ethernet frame into the frame of the Token Ring.
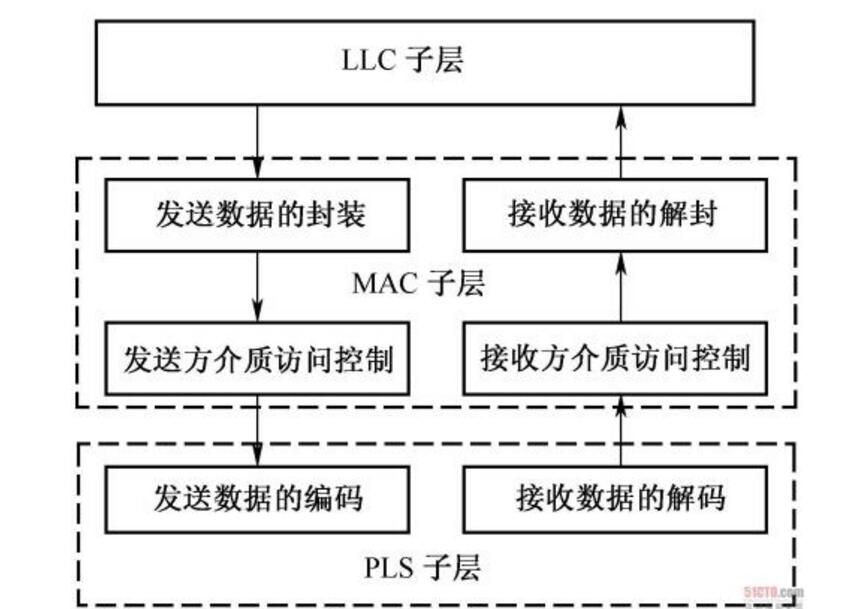
The MAC sublayer is responsible for grouping the "0" and "1" bitstreams of the physical layer into frames, and performing error checking by error check information at the end of the frame; providing access methods for shared media, including collision detection with Ethernet Carrier sense multiple access (CSMA/CD), TokenRing, Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI), etc.
The MAC sublayer allocates a separate LAN address, which is commonly referred to as a MAC address (physical address). The MAC sublayer adds the physical address of the target computer to the data frame. When the data frame is delivered to the MAC sublayer of the peer, it checks whether the address matches its own address. If the address in the frame does not match its own address. Matches, discards this frame; if it matches, it is sent to the previous layer.
The difference between the MAC sublayer and the LLC sublayerThe MAC (Media Access Control) sublayer defines how packets are transmitted over the medium. In a link that shares the same bandwidth, access to the connected medium is "first come, first served." Physical addressing is defined here, and the logical topology (the path through which the signal passes through the physical topology) is also defined here. Line control, error notification (not corrected), frame delivery order, and selectable flow control are also implemented at this sublayer.
Note: This protocol is located in the data link layer of the OSI Layer 7 protocol. The data link layer is divided into upper layer LLC (logical link control) and lower layer MAC (Media Access Control). The MAC is mainly responsible for controlling and connecting the physical layer physical layer. medium. When transmitting data, the MAC protocol can determine in advance whether data can be sent. If it can be sent, some control information will be added to the data, and finally the data and control information will be sent to the physical layer in a prescribed format; when receiving data, MAC The protocol first determines the input information and whether a transmission error has occurred. If there is no error, the control information is removed and sent to the LLC (Logical Link Control) layer.
Applications: Whether in traditional wired local area networks (LANs) or in the current popular wireless local area networks (WLANs), the MAC protocol is widely used. In the traditional local area network, the physical layer of various transmission media (copper cable, light, etc.) corresponds to the corresponding MAC layer. Currently, the commonly used network adopts the MAC layer standard of IEEE802.3, adopting the CSMA/CD access control mode; In the wireless local area network, the standard corresponding to the MAC is IEEE802.11, and its working mode adopts DCF (distribution control) and PCF (central control).
Logical links are a protocol-driven communication session between two end systems that exchange communication information on actual or logical circuits. The protocol stack defines the communication of two systems on a medium. A variety of different types of communication protocols are available at the lower level of the protocol stack, such as local area network (LAN), metropolitan area network (MAN), and icon X. 25 or a packet switched network such as Frame Relay. A logical link is formed between two communication systems on a physical link, which can be copper wire, fiber optics, or other medium. According to the OSI protocol model, these logical links exist only above the physical layer. You can think of a logical link as a line that exists between two networked systems in the network.
The main features of the LLC sublayer include:
* Transmission reliability guarantee and control;
* Segmentation and reorganization of data packets;
* Sequential transmission of data packets.
The main functions of the MAC sublayer include data frame encapsulation/unloading, frame addressing and identification, frame reception and transmission, link management, frame error control, and the like. The presence of the MAC sublayer masks the differences in the types of different physical links.
Semiconductor Plastic Package.Refers to the material whose conductivity is between the conductor and the insulator at room temperature. Semiconductors have a wide range of applications in radios, televisions, and temperature measurement. Diodes are semiconductor devices. Semiconductor refers to a material whose conductivity can be controlled and can range from insulator to conductor. Regardless of technology or economic development, the importance of semiconductors is enormous. Most of today`s electronic products, such as computers, mobile phones or digital recorders, have core units that are very closely related to semiconductors. The common semiconductor materials are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, etc., and silicon is a kind of most influential one among various semiconductor materials in commercial applications.
Semiconductor Plastic Package,Semiconductor Package,Silicon Transistor,Bi Directions Thyristor
YANGZHOU POSITIONING TECH CO., LTD. , https://www.cnchipmicro.com
