First look at the drive of the relay
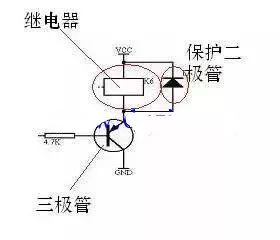
This is a typical relay drive circuit diagram. Such a picture can be found anywhere on the network, and it is generally the same in standard textbooks.
Why understand the principle of this diagram?
The MCU is a weak device. Under normal circumstances, most of them work at 5V or lower. The drive current is below the mA level. To use it in some high-power applications, such as controlling the motor, it is obviously not feasible. Therefore, there must be A link to connect, this link is called "power drive". Relay drive is a typical, simple power drive link. Here, the relay drive has two meanings: one is to drive the relay, because the relay itself for the microcontroller It is a power device;
There is also a relay to drive other loads, such as relays can drive intermediate relays, can directly drive the contactor, so the relay drive is the interface between the microcontroller and other high-power loads. This is very important, because, always let our electrical engineers (I mean What puzzles those who haven't learned the corresponding electronic technology is: How can a small chip have such powerful power to control something as powerful as an electric motor?
How to understand this circuit diagram?
To understand this circuit, it is actually quite easy. Then please follow my thoughts, there should be no problem:
First of all, the triode inside is very important. The triode is a very important component in electronic circuits. How to understand the triode?
Simply speaking, the triode has two functions: one is amplification and the other is switching. (Strictly speaking, the switching function is the limit of amplification, but it does not matter, separate the two, it is easier to understand its working principle). Here, we only understand the switching effect associated with this circuit.
First think of the triode as a tap.
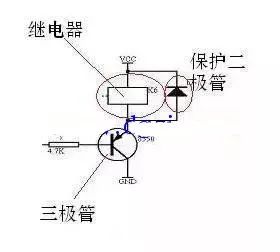
The above Vcc is the pool, the relay is a water turbine, and the GND below is any point lower than the pool. As I said earlier, the triode is the faucet, and its handle is the one with a resistor.
Now, one of the MCU needs to control the output pin of this relay circuit is a "hand". When this pin of the MCU outputs a low level, it is like "hand" in opening the triode "faucet", the water is from Up and down, the relay "turbine" starts to turn. Conversely, if the output is high, the "hand" will start to turn off the "faucet", and the relay "turbine" will stop because there is no water flowing down.
This is the switching effect of the triode.
The simple understanding and memory is that the triode is a switching device. In fact, you can really think of it as a switch, but it is not controlled by hand, but by voltage (current). Therefore, some triodes are It is also called an electronic switch (different from mechanical switches).
There is another thing on the picture, it is a protection diode. If you don't need to understand it in depth, you don't have to chase why it exists, but you must remember that as long as it is driven by a triode, it usually has its existence. What needs special attention is its connection method: the cathode at both ends of the relay must be connected to Vcc.
Ethernet cables connect devices such as PCs, routers, and switches within a local area network.Most technicians refer to these standards as CAT5 and CAT6, respectively. Also CAT3 available. Because of this, many online stores that sell network cables use this abbreviated language as well.
The connector can by shield or non-shield type, raw cable can be UTP, STP, FTP type. Also the molded shape can be custom mould by straight, right-angle, 105 degree, etc.
These physical cables are limited by length and durability. If a network cable is too long or of poor quality, it won't carry a good network signal. These limits are one reason there are different types of Ethernet cables that are optimized to perform certain tasks in specific situations.
Ethernet Cable Wiring,RJ45 cable,networking cable,8P8C cable
ETOP WIREHARNESS LIMITED , https://www.oemwireharness.com
