As sales prices plummet, microcontroller companies are looking for new ways to achieve economies of scale.
Microcontrollers are being used as a powerful competitor to a wide range of new and far more complex computing tasks, moving from a single chip to a more highly integrated device.
The microcontroller unit (MCU/microcontroller) can be used for many tasks, from assisted driving and automatic driving to smart cards. They are often the central processing components of various interconnected devices; these interconnected devices are gradually forming the Internet of Things. In fact, if there is no MCU, it will not be easy to say if the Internet of Things can succeed.
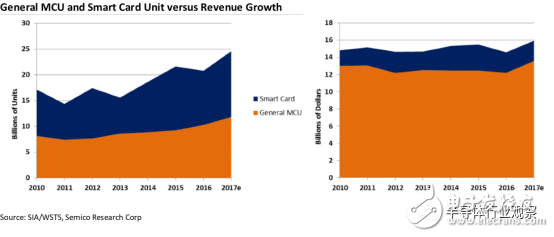
Figure 1: MCU demand is growing healthily, but overall market revenue growth is much slower. From Semico Research
But this popularity has a price. Although the market opportunities for MCUs are expanding, the average selling price has fallen sharply. The shipments required to recover development costs are now much larger than before, and some companies may find it difficult to continue to make money in the MCU sector without making major changes.
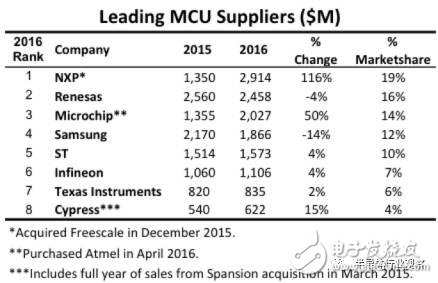
Figure 2: The biggest growth in the MCU industry in the report comes from consolidation. From IC Insights
There are three main types of microcontrollers: 8-bit, 16-bit, and 32-bit. There are still some 4-bit microcontrollers in use, but many 4-bit microcontroller customers have either migrated to 8 or plan to migrate in the future. The 16-bit MCU will be the next mainstream, which is also more expensive. But the price of 32-bit MCUs has dropped so fast that most customers who are considering upgrading to 16-bit are now moving to more advanced chips.
Rob Lineback, senior market research analyst at IC Insights, said: "This year, 32-bit ASP (average selling price) fell by 15%. We see a 32-point price drop of 7% per year (CAGR / compound annual growth rate). 16 The market's CAGR is -2%, and the 8/4 market is also -2%. In the future, it will be possible for 32-bit microcontrollers to sell at a lower price than 16-bit microcontrollers. This is pure competition and pricing. Stress. The Internet of Things is part of the driving force."
Joanne Itow, general manager of manufacturing at Semico Research, also saw a similar trend: "In addition to DRAM and NAND, ASP in all logic chip markets is not doing well now. The only big winner in the microcontroller market is ARM because they control the core. Low-power IP and security. Companies can develop all of these things themselves, but it's easier to use ARM."
The same problem, different strategies
There are currently two conflicting trends in development – ​​ASP is falling and complexity is rising. This puts much more pressure on MCU manufacturers who need to make their processes and methods more efficient.
One way is to take advantage of what is already in these devices, but many companies are ignoring this approach. “Look at TrustZone, many of which are useless,†said Andrew Caples, senior product line manager for embedded software at Mentor, a Siemens company. “You can increase reliability and create memory partitions so you can read or write. But it doesn't make full use of it. Power management is another feature, which in some cases may be a decisive factor in how well a product performs, because it affects battery life. Some of these MCUs have more than 16 low power. State, but migrating from one power state to the next is very complicated. To take advantage of these features, you need to invest far more in software."
The increase in complexity has already allowed MCU manufacturers to migrate to the next process node, which allows more memory, connectivity and processing power to be integrated in the same size space. This is the application of Moore's Law in a different market, and for 32-bit MCUs, the current leading edge node is 40nm. The company is also developing a 32/28nm version.
Geoffrey Tate, CEO of Flex Logix, said: "The problem is that microcontroller companies have developed dozens or even hundreds of SKUs (stock-keeping units), in part because the pins assigned to serial I/O are different. Is SPI (serial peripheral interface), some are UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter). Or they provide hardware and binding in different ways. But the 40nm mask cost will rise, so dozens of variants will It consumes a lot of money. A certain number of lookup tables are required to program a serial I/O."
One way to circumvent this problem is to use embedded FPGAs to increase the flexibility of the microcontroller itself so that these devices can meet the programming needs of different markets without having to develop a new MCU for each application. .
The third method is to do more efficient verification and reduce the amount of time required for the back end of the MCU design flow.
Frank Schirrmeister, senior director of product management and marketing for simulation, FPGA-based prototyping and hardware/software enablement at Cadence, said: "This is why Portable Stimulus is interesting. It makes it easier for us to understand. These Some of the MCUs are becoming more like systems, so some microcontroller companies are selling these designs with custom software development. This can be used to evaluate them."
One device, multiple uses
All of these methods help turn the MCU into a ready-to-use device that can be quickly customized for vertical market segments or specific applications. But the entire process needs further simplification.
Bill Neifert, senior director of market development at ARM, said: "In EDA, you are more tolerant of some of the oddities in the tool. Look at the microcontroller market, but it's very different, because people who develop software want to download the debugger. And the compiler and it works. Their final product is not a chip. It's a system, they need something that can effectively solve their problems. You provide a reduced size device with a lot of features and options, so You need to meet everyone's needs, from the most advanced users to amateurs who develop disposable products. The same products need to be suitable for all of them."
The key is to find a balance between time to market and cost and optimization. This balance may also vary significantly depending on the application.
Semico's Itow said: "There are some different approaches to this. Some companies are designed for specific applications, such as IIoT. Some companies believe that the general approach is the right approach and then customize it around it. But obviously there are various Different opportunities. So even if we are seeing some integration, we are very likely to see new companies entering this market."
The real thing is the Internet of Things and consumer electronics markets, and MCUs are tailored for these segments. They include memory, processing, security, and communication technologies, but all of them are weaker than powerful SoCs.
“In the past, a large number of microcontrollers were eventually used in the industrial and automotive markets, and these markets have longer sales cycles,†Neifert said. “Now we see that they are increasingly used in the consumer electronics market, where Content needs to be up-to-date and best. As more and more such devices are sold to consumers, you will need a fast turnaround, which means that the same microcontrollers may have 10 different applications, and Many of them depend on the software."
Some of them will be applied to systems that have never existed before, or as a general-purpose add-on to the system, not to the core of the architecture.
Bill Hutchings, senior product marketing manager at Microchip Technology, said: "There are some higher performance cores and clocks that are usually microprocessor-independent. So look at the sensor hub, usually with a preprocessor, usually used as the middle tier. Microcontroller."
Redefine the MCU
The differentiation factor between microcontrollers over the past few years has been functional. Therefore, 32-bit MCUs are significantly more powerful than 8-bit MCUs, so the price is higher. But as the company moved up, they are now developing devices that rival the low-end microprocessor product line.
But historically, there are still significant differences between the two. Microprocessors use both internal and external memory in combination, whereas traditional MCUs rely only on internal memory. This situation is beginning to change, and some MCUs offer the ability to connect to DRAM or other types of external memory.
“If you go back 15 years ago, you find 100 engineers and put a microcontroller and a microprocessor in front of them, they can definitely tell which one is which.†Rambus’s distinguished inventor Steven Woo said, “If There are a lot of controversies when you find the same 100 engineers today. Moore's Law is part of the reason for this ambiguity. There are more transistors on the die, and you can do more with these transistors. too much."
With better space utilization, we can also put more on-chip and off-chip memory. MCUs typically use a combination of DDR2 and flash memory. But because the density has increased everywhere, the memory size of DDR2 has increased to 2MB, and there is 2MB of embedded flash memory.
“From at least 6 or 7 years, devices on the 32-bit product line already have the ability to connect to external memory, but not many devices take advantage of this.†Stuart McLaren, Microcontroller Product Manager, Americas, STMicroelectronics Says, "We have seen this recently (using the system packet interface), so there are more NVMs outside to store data and code. The key change is more performance and more features. There will be more and more applications, and as they become interconnected, you will have nodes that communicate with the gateway or the cloud. At least a simple microcontroller is needed to collect some sensor data and aggregate it into together."
The microcontroller is also beginning to move upstream of the cloud.
“There are a lot of cloud services running on the gateway, and they are doing more advanced analytics,†McLaren said. “We saw external memory for graphics processing, usually a 1 or 2 frame buffer, you can Here we render the information from the frame buffer and then refresh it. We can also see that a large number of microcontrollers enter the three areas of the Internet of Things - home and city, smart industry, smart everything. Every application has processing and security. Requirements. They also need to interface with real work and require some form of connection. In many cases this connection is RF, but it can also be low-power Bluetooth or other near-field processing. And they need to manage power, from Wearable to industrial applications is possible. MCU is the core of the Internet of Things."
According to Dipesh Patel, vice president of physical IP engineering at ARM, MCUs will also be used in new applications such as asset tracking. "With 32-bit, you can track the journey of a component, and you can make it completely secure. You can never do this with 8 bits. MCUs are getting more and more complex. On a simple level, you can store Process and transfer data. But now you can do more because there is more memory."
He pointed out that there is now an increase in on-chip flash memory, especially as some of the more advanced designs are moving to 40nm or even 28nm. Today, most MCUs use older processes, some even up to 350nm, but some of the more advanced IoT designs are developed in 65nm and 40nm processes.
Mass customization and niche
Cost has always been one of the key drivers of MCUs, and although the primary consideration for using them over the past decade has been power characteristics, it is difficult to find systems without microcontrollers. But gradually, system vendors have also begun to design MCUs for new tasks, and just a few years ago, system vendors did not consider these tasks at all.
“We saw them being used as companion chips for fully integrated microprocessors and for security applications,†said Jeanette Wilson, product marketing manager at Microchip. “You may need to do basic authentication, and microcontrollers can be Used as a hardened key memory. This requires a handshake with an ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography) SoC, which you can put into a tamper-proof package or use as an entropy source. You can also add encryption/decryption, which is another level of security and has a monotonic counter to prevent replay. This is usually done in software, but if you do it in hardware, you can save 8000 Up to 12,000 lines of code, and from an execution point of view, this will be faster."
MCUs are also appearing on expansion boards and next to sensors that measure a wide range of metrics, from motion to temperature.
STMicroelectronics' McLaren said: "We run them at frequencies up to 400MHz. In the past, you only saw this speed on the MPU. And we also saw some cases where the microcontroller itself is connected to multiple microcontrollers. There may be an API between the main microcontroller and other microcontrollers."
to sum upThe difficulty of distinguishing between different types of logic devices is growing, and as advanced packaging continues to be used for more designs, this difficulty may continue to increase.
IC Insights' Lineback says: "In the 1980s, MCUs were system on a chip or computer on a chip, and sometimes people say that directly. Finally, define these categories of WSTS ( The World Semiconductor Trade Statistics Organization will draw different boundaries."
At the same time, MCU vendors will do their utmost to increase the value of their devices and delay the price decline, as the trend of price cuts has brought severe technical challenges to the industry. Will they add more flexibility to the device, or reduce the number of devices currently being developed, or change the way these devices are designed and verified? It is still unclear. But the importance of MCUs will only grow larger, so these issues will also need to be addressed.
Fast Recovery Diode is a semiconductor device which possesses short reverse recovery time for rectification purpose at high frequency. A quick recovery time is crucial for rectification of high-frequency AC signal. Diodes are mostly used in rectifiers because they possess ultra-high switching speed.
Fast Recovery Diode,Fast Recovery Rectifier Diode,Super Fast Recovery Diode,Fast Recovery Epitaxial Diode,Recovery Diode
YANGZHOU POSITIONING TECH CO., LTD. , https://www.cnfudatech.com
