The Circuits from the Lab reference circuit is a tested reference design that helps accelerate design while simplifying system integration to help and solve today's analog, mixed-signal and RF design challenges.
Connection/reference device
ADF4351
35 MHz to 4400 MHz wideband frequency synthesizer with integrated VCO
ADL5801
10 MHz to 6 GHz wideband active mixer
AD8368
800 MHz, linear dB VGA, built-in AGC detector
ADL5902
50 MHz to 9 GHz, 65 dB TruPwr? Detector
Frequency selection, RMS response, 90 dB dynamic range, 35 MHz to 4.4 GHz RF detector
Circuit evaluation board
ADF4351 Evaluation Board (EVAL-ADF4351EB1Z)
ADL5801 Evaluation Board (ADL5801-EVALZ)
AD8368 Evaluation Board (AD8368-EVALZ)
ADL5902 Evaluation Board (ADL5902-EVALZ)
EPCOS B5249 SAW Filter Evaluation Board or equivalent
Circuit function and advantage
This circuit is a frequency-tunable radio frequency (RF) detector that provides a 90 dB detection range from 35 MHz to 4.4 GHz. Unlike independent detectors that do not distinguish between signals in the spectrum, this circuit can focus on a narrower frequency band to provide enhanced performance over a specified range. The detector circuit provides RMS response with excellent temperature and frequency stability and is attractive for applications that require precise frequency and selective RF power measurements. This circuit also suppresses unwanted blocking signals very well. Figure 1 shows the schematic diagram of the circuit.
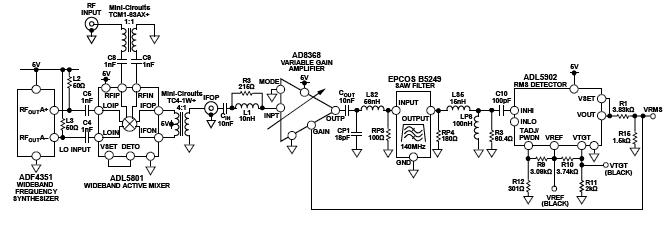
Figure 1. Frequency selective RF detector
Circuit description
The detector circuit consists of an RMS detector, variable gain amplifier (VGA), SAW filter, mixer, and frequency synthesizer, providing a 90 dB detection range and excellent frequency/temperature stability. Figure 2 shows the transfer function of the detector circuit when the input power is scanned at 900 MHz. The best linearity is obtained with a 4-point calibration method with +13 dBm, ?50 dBm, ?65 dB and ?75 dBm. A 2-point calibration can also be used, but the linearity will decrease over the input power range.
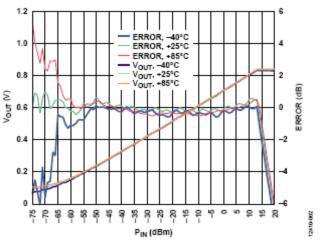
Figure 2. Transfer function of a frequency selective RF detector at different temperatures
Dynamic range enhancement
The ADL5902 detector used in the circuit itself provides a detection range of 65 dB and operates from 50 MHz to 9 GHz. The AD8368 VGA extends the upper and lower limits of the power range. The narrowband SAW filter between the VGA and the detector filters out the noise of the VGA and mixer, maximizing the lower sensitivity. Circuit Note CN-0340 illustrates this dynamic range extension mechanism in more detail. However, this range expansion limits the operation of the filter passband frequency range. The broadband frequency conversion network combined with the CN-0340 circuit allows the entire circuit to have frequency selection characteristics. In the circuit shown in Figure 1, the ADL5801 mixer is paired with the ADF4351 frequency synthesizer to convert the input signal from 35 MHz to 4.4 GHz to 140 MHz, the passband frequency of the SAW filter. Circuit Note CN-0239 illustrates the seamless wideband mixer and local oscillator interface used in this circuit.
The dynamic range of the circuit is further enhanced by optimizing the mixer bias level using the VSET pin of the mixer ADL5801. Typically, the ADL5801 mixer operates at a VSET level of 3.6 V, resulting in a higher mixer bias level and a correspondingly high IP3. However, this operating point can cause noise figure degradation, which limits input sensitivity. The mixer operates at a minimum VSET level of 2.0 V to improve the noise figure, but this affects the mixer's P1dB and limits the upper limit of the dynamic range. Therefore, the mixer needs to adopt an adaptive biasing mechanism to optimize the circuit detection range at both high and low power levels. By connecting the VSET pin to DETO (a pin routed to the internal power detector of the mixer), the device bias level can be adaptively set according to the signal conditions. With this feature, the mixer provides high linearity and compression for large RF signals while providing low noise figure for small RF signals. This feature improves the sensitivity of applications at lower input power levels while maintaining dynamic range at higher input power levels. Figure 3 shows the transfer function of the detector at different mixer bias levels.
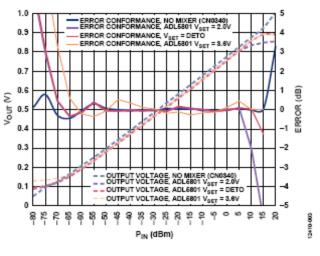
Figure 3. Performance comparison of ADL5801 mixers at different bias levels
Anti-rat ant Solar Cable is a kind of cable specially used for photovoltaic power generation system, its main function is to prevent small animals such as mice and ants from destroying the photovoltaic line.
The characteristics of anti-rat ant solar cable are as follows:
1. Anti-ant performance: anti-rat ant solar cable adopts special materials and technology treatment, has strong anti-ant performance, and can effectively prevent the invasion of ants and other small animals.
2. Anti-bite performance: anti-rat ant solar cable has good anti-bite performance, can resist the bite of mice and other animals, to avoid short circuit, fire and other safety hazards.
3. Weather resistance: anti-rat ant solar cable is made of high-quality materials, has good weather resistance, and can run stably for a long time under various harsh environmental conditions.
4. Easy installation: The installation method of anti-rat ant solar cable is the same as that of ordinary light cable, without additional tools and equipment, easy and quick installation.
5. Efficient performance: anti-rat ant solar cable has low resistance and high conductivity, which can ensure the efficient operation of photovoltaic system.
In short, the anti-rat ant solar cable is a kind of cable specially designed for photovoltaic power generation system, with the characteristics of ant-proof, anti-bite, weather resistance, easy installation and efficient performance, which can effectively protect the solar cable from the damage of small animals such as mice and ants.
Anti-Mouse Ants Solar Cable,Adapter Cable,Ant Rat Resistant Solar Cable,Ant Resistant Dc Cable
Suzhou Yonghao Cable Co.,Ltd. , https://www.yonghaocable.com
