The new in-vehicle infotainment system and navigation system provide more content, allowing you to experience higher quality audio and video programming and improve the connectivity of personal communication devices. In order to adapt to the high data transmission rate and meet the requirements of current communication, it is necessary to protect such equipment from damage caused by customer misuse, dangerous environment and power fluctuations.
This article refers to the address: http://
Self-resetting PPTC (Polymer Positive Temperature Coefficient) devices are widely used in infotainment systems to protect precision electronic components and peripherals. In applications where the self-recovery function is not desirable or practical, a chip surface mount fuse is typically used.
Infotainment devices are also susceptible to damage due to excessive transient voltages, including the working environment in which they are located and the electrostatic discharge (ESD) pulses generated by peripheral devices. ESD protection devices, metal oxide varistor (MOV) and Zener diodes are often used to protect automotive electronic devices such as antennas, backlight heaters, batteries, buttons, printed circuits on circuit boards, CD/DVD players, data lines Ports, hard drives, and input/output ports and touch screens.
Design considerations for automotive circuit protection devices
# PPTC overcurrent / overheat protection
The popular PPTC device has a self-resetting function that can be mounted in an easily accessible location in a car. It has a wide range of products with different electrical properties and sizes to facilitate a variety of precise protection designs. When selecting a PPTC device, the main consideration is that the device's holding current rating is matched to the primary current of the device during normal operation.
# ESD protection device
High-speed input/output ports require the use of small-capacitance ESD protection devices to keep signal quality as low as possible. The device chosen should be suitable for high-speed data transmission lines and radio frequency data lines, capable of withstanding numerous ESD transients. To meet the requirements of RoHS and IEC61000-4-2, the capacitance is small, the trigger voltage is low, and the response time is short. These are also important features of ESD protection devices.
# Surface Mount Fuse
Surface mount fuses with large currents and small sizes have both fast and slow fuses, and their fuse characteristics should be clean, including the fuse process should be carried out inside the package. Their ability to suppress arcing should be good and able to withstand shock and vibration.
# 金属氧化å˜å˜å™¨
Metal oxide varistors (MOVs) are available in a variety of diameters and voltage ranges. MOV devices can flow a large amount of current and absorb a large amount of energy to achieve overvoltage protection. When selecting MOV, it is based on the clamp voltage level (suppressed voltage rating) and response time.
DC power port protection
The car power bus is very dirty, which is known to everyone. The car's power supply is rated at 12V, but will vary from 8V to 16V during normal operation. Also, the current of the battery will exceed 100 amps, and it will be interrupted by the action of the relay or the fuse is blown. Therefore, a large induced voltage spike is generated on the power bus, and the voltage is increased by more than 5 times.
During the operation of the car's power supply, it may be damaged by a battery connection error or when it is connected to a battery with twice the voltage (24 volts) when the dual battery is started. There is a situation called "load dumping" which can generate very high voltages on the power bus. A typical third-party power converter will filter it out, but tests by Tyco Electronics show that the ability of these power converters to reject transient voltages varies greatly. Devices that typically charge the USB interface are generally not designed for this type of voltage fluctuation and therefore require overvoltage protection.
The demand for overcurrent and overvoltage protection in portable devices that are being recharged in the car is growing, and Tyco Electronics' new PolyZen® devices are able to meet its needs. When used with a Zener diode-like protection device, this device has a synergistic protection against high power fault conditions.

Figure 1: PolyZen devices protect the input power, DC power, and output power conditioning circuitry of automotive peripherals.
As shown in Figure 1, the miniature PolyZen device contains a stable Zener diode and a non-linear resistive PPTC layer. The Zener diode precisely clamps the voltage, and the resistive PPTC layer responds to the diode's heating or overcurrent events, transitioning from a low resistance state to a high resistance state.
PolyZen devices are particularly effective for clamping and smoothing inductive voltage spikes. In the presence of an inductive spike, the Zener diode bypasses the current to ground until the voltage drops to the normal operating range. In the case of a supply voltage error, the PolyZen device clamps the voltage and bypasses excessive current to ground to prevent power supply errors. The voltage and current response characteristics of PolyZen devices are relatively flat, which helps clamp the output voltage, even if the input voltage and supply current vary.
Because the current can be very large in automotive applications, be careful and ensure proper protection. For the selected device, check its IFLT maximum and Vout peak to ensure that the device provides the required protection.
PCB board for protecting electronic modules
The market demands more electronics and more internal space. In response to this demand, automakers are putting more circuits into smaller packages. In order to provide more and more functions and connections with smaller and denser printed circuit board areas, the printed line width on the board must be reduced.
Many of these control modules are "black boxes" that are now used to control an increasing number of high-power accessories, such as power windows, power seat adjustments, remote door locks, and radios and GPS antennas. Because the power supply for these accessories is provided by a circuit with a large current, the possibility of burnout increases because the printed circuit on the printed circuit board is very thin and a large current flows. This situation is possible. For example, if a power ground is disconnected from the load, its current will flow through a small printed line on the board, and the current in this trace will increase.
The printed lines on the printed circuit board function to carry current from one place to another. The current that can flow through each trace depends on its cross-sectional area. The maximum current is the heat generated by the I2R power dissipation that does not blow it off. Even if it has not melted, it may be hot enough to damage the printed circuit board or damage some of the components mounted on it.
Self-resetting PPTC devices are often used to protect these tiny printed lines on the board because such devices can quickly and efficiently limit current to safe values ​​and are small enough to fit directly onto the board. Using this technology, each individual power supply circuit in the module can be protected with a PPTC device, limiting the current to a safe value without blowing it.
The fuse and PolySwitch devices are compared in Figures 2 and 3. Here we assume that the board designer sets the maximum temperature of the printed line at 100 °C. Therefore, as the temperature of the printed line approaches 100 ° C, the current that can flow over it becomes smaller and smaller.
The example shown in Figure 2 is a 1 oz (35 μm), 100 mil (2.5 mm) printed line that is protected with a plug-in PolySwitch® device AGR500. In Figure 3, the width of the trace is reduced to 20 mils (0.5 mm) and protected with a PolySwitch series surface mount device ASMD150.
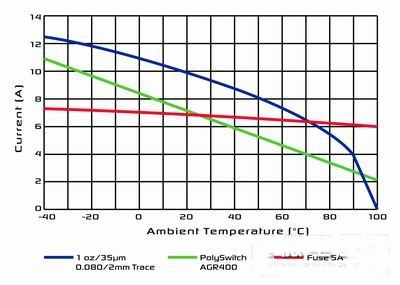
Figure 2: The performance of the fuse and PolySwitch device AGR500 is compared.
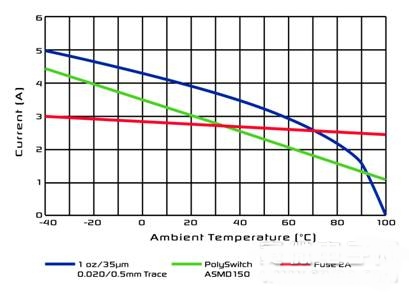
Figure 3: The performance of the fuse and PolySwitch device ASMD150 is compared.
It must be noted that the trigger current of the PPTC device follows the current on the trace over the entire temperature range. In both cases, even if a fuse can be used, the closest fuse can't protect it when the car is above the useful standard temperature.
PPTC circuit protection devices are widely used as a practical, cost-effective solution for overcurrent and/or overtemperature protection in electronic modules. This device is often used to limit current in GPS, DVD or radio and telematics boards.
summary
There are now a variety of innovative circuit protection solutions, with a variety of sizes and a variety of soldering end products, which can help automakers and portable equipment manufacturers meet the stringent requirements of automobiles, improve equipment reliability, and enhance end-users. Convenience and satisfaction. With overcurrent, overvoltage, and ESD synergy, you can reduce component count and increase the efficiency and reliability of your electronic components and networks.
The Marshine line of Hydraulic Puller and Tensioners provides utilities and utility contractors the ability to improve productivity and efficiency while limiting downtime and improving job site safety. Hydraulic Puller and Tensioners from Marshine represent the next generation of stringing equipment. Features like negative self-acting hydraulic brakes, integrated hydraulic dynamometers, hydraulic cooling systems, advanced user controls and more make Marshine Hydraulic puller and tensioners the safest and most effective on the market today.

Hydraulic Cable Puller,Hydraulically Limited Cable Puller,OMAC Hydraulic Cable Puller,Fiber Optic Cable Pullers,Stringing Equipment Hydraulic Cable Puller
MARSHINE , https://www.puller-tensioner.com
