Just five years ago, the self-driving car seemed to be far away from us. At this year's CES, live demonstrations, products, and manufacturers related to autonomous driving occupied the media layout. In fact, 13 of the world's 14 largest automakers have announced that they will introduce autonomous vehicles to the market; 12 of the world's 14 largest technology companies have announced that they will develop technologies related to autonomous driving.
The sudden interest in autopilots in the market has also made autopilots more sought-after, and the price of such talents can even reach $10 million. Harvard, MIT, Carnegie Mellon and Stanford students pay attention!
Obviously, many large companies are investing heavily in autonomous driving because they believe that autonomous driving will dramatically change the automotive industry, and they see the power of social culture that is driven by autonomous driving. If we spend more time in the car in the future, then the car will be a bigger business, and these companies want to share a piece of it.
What investors are most interested in is understanding how companies in the industry chain develop their competitive strategies in the autonomous driving market. For example, do automakers develop their own autopilot technology, rely on partners, or both? Will automakers sell autonomous vehicles to consumers, or simply provide them to a taxi platform for shared travel services? Will the shared travel service company want to enter the autonomous driving field?
Changing value chainHere is the author's view of the current autopilot industry value chain. The three high-value levels of the autopilot market are
1. Service provider (eg shared travel company, car rental company)
2. Technology provider (including software and hardware level)
3. Car manufacturer

As you can see from the picture, there are many companies that have two identities—such as Tesla's automaker system as a car manufacturer. At the same time, companies that used to focus on only one area have invested a lot of capital and time in other areas to extend to other levels of the value chain. An example of this is ReachNow, BMW's rental and ride services. Sharing travel in the future may have an impact on the sales of “personal carâ€. BMW chooses to bet on both sides to avoid being squeezed out of the market.
These companies have the opportunity to gain a larger share of the final value chain of the autonomous driving industry, and they are positioned and adjusted accordingly.
Autopilot Cooperation Matrix: Solving Risk through CooperationIn addition to investing in and acquiring other companies and talents, companies in the autonomous driving industry are actively looking for partners to avoid falling out of high-value chains or to circumvent the risks posed by core technology vendors.
For example, these companies realize that high-precision maps may be one of the most critical technologies for autonomous driving, and they can assist autonomous vehicles in determining the position of cars, people, and other objects. This has led to several major moves in the industry, including the development of maps of their own homes or the purchase of map data for other homes. In August 2015, Mercedes-Benz BMW Audi jointly invested $3.2 billion to acquire High Precision Maps Here; in July 2016, Uber announced that it would invest $500 million to collect road data from around the world; in December 2016, Mobileye announced A partnership with Here, the two sides share map data.
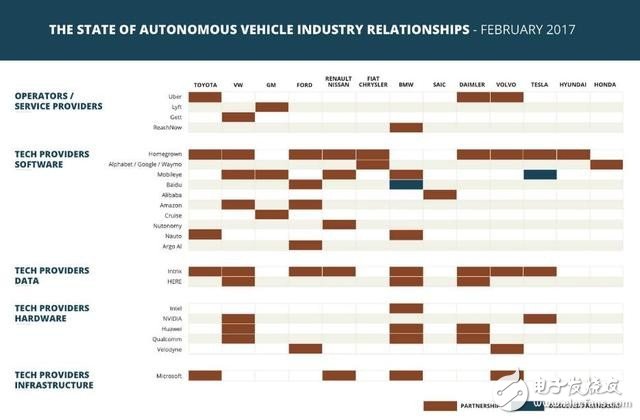
1. Automakers working with major technology providers are also developing their own self-driving systems. For example, although Volvo provided Uber with its SUV for autopilot testing in Pittsburgh, San Francisco and Arizona, Volvo is still working on the Drive Me project to develop its own autonomous driving system.
2. The cooperation in the autopilot industry has also experienced some emotional breakdown and “breakupâ€. After Tesla’s death in a car accident, Tesla and Mobileye were arguing who was fired (and whose technology led to the car accident). BMW and Baidu also terminated cooperation due to inconsistencies in development pace and research philosophy. In the future, more companies may solve technical and business problems in an independent manner.
3. Most automakers have entered the ride market, whether it is Toyota and GM investing in Uber and Lyft models, or a wholly-owned acquisition model, or launching their own ride. These moves are very interesting, because in the era of autonomous driving, Uber and Lyft's core resources - drivers, seem less important. When autonomous vehicles are put into the service, other aspects will become more important success levers – such as production capacity, financial management, and operational capabilities. This is the advantage of car manufacturers. It can be said that this will enable automakers to work in the late stage. However, the success of the ride market also depends on the penetration rate among consumers, so companies like Uber and Lyft can also build influence in the autonomous driving industry.
Regulator attitudeFocus on the industry, in addition to software development companies and car companies, as well as regulators, drivers, and ordinary consumers.
So far, the attitude of autonomous driving technology in the United States is not bad. From the bottom up, regulators and planners at multiple levels seem to realize that autonomous driving will result in fewer accidents, less congestion, less commute time, and less parking space for urban space. But they are taking a cautious approach to encourage companies to conduct automated driving experiments in a safe and controlled manner. When the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration investigated Tesla’s fatal car accident, they found that although the autopilot function gave the owner a life (the owner violated the rules to use automatic driving), Tesla’s autopilot function has been introduced since its introduction. The frequency of car accidents has been reduced by 40%.
On the other hand, as the technology becomes mainstream, it will be widely adopted by the public ride market and truck companies, which can cause enormous damage to the labor structure in many places. US 2015 census data shows that truck drivers are almost the most common job in every state in the country. Automated driving technology will have a huge impact on the truck industry.
As more and more startups and large companies begin to showcase and release their autonomous driving-related products, they must find the right way to introduce autonomous driving technology that is both public safety and publicly aware. People always have a sense of distrust of things that are not controlled by themselves (especially autopilots, which are life-saving technologies). These companies need to spend a lot of time trying to convince society to accept autonomous driving.
However, the autopilot market is growing at a rapid rate, and its expansion rate has doubled in the past five years. At this rate, what will it look like in five years? Maybe not even five years, as long as two and a half years.
Gaming mechanical keyboard,Gaming RGB keyboard,gaming keyboard custom,ergonomic gaming keyboard
Dongguan Yingxin Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.dgyingxintech.com
