The early IoT refers to the transmission of data between two or more devices in close range, to solve the connection of objects, the early use of wired mode, and the later use of wireless mode; with the progress and development of the times, the society gradually Entering the Internet +, the data collected by various types of sensors is becoming more and more abundant, and the application of big data comes along. People consider integrating various types of devices directly into the Internet to facilitate data collection, management, and analysis and calculation.
In short, the intelligence of the Internet of Things is no longer limited to small devices, small network stages, but to the complete field of intelligent industrialization, intelligent Internet of Things is mature in big data, cloud computing, virtual reality, and Incorporate the Internet + the entire ecological environment.
Common IoT communication methodsCommonly used IoT communication methods can be divided into four categories, as shown in the following figure:
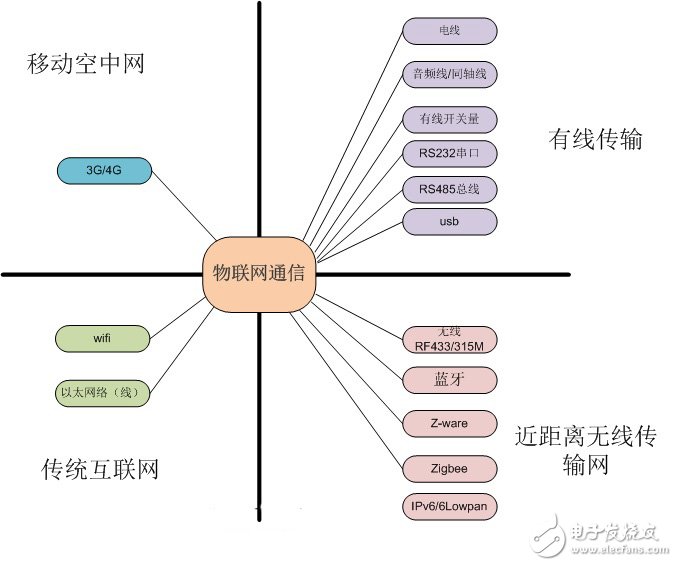
It is not very convenient to connect the devices directly with physical lines. Mainly have wire carrier or carrier frequency, coaxial line, switch signal line, RS232 serial port, RS485, USB, here only introduce the commonly used RS232 serial port, RS485, USB.
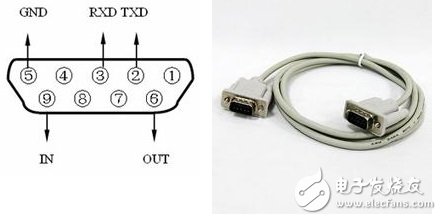
RS232 serial port: Serial communication interface, the full name is "the serial binary data exchange interface technology standard between data terminal equipment (DTE) and data communication equipment (DCE)", which is a standard interface for transmitting information between computers and other equipment; The standard specifies a 25-pin DB25 connector that specifies the signal content of each pin of the connector and also specifies the level of various signals. RS-232 is a single-ended signal transmission. Noise and the problem of not being able to suppress common mode interference, so it is generally used for communication within 20m. The commonly used serial line is generally only 1~2 meters. See picture:
RS-485 bus: RS232 cannot be satisfied when the communication distance is required to be several tens of meters to kilometers, or when there are multiple devices networking requirements, so the RS-485 serial bus standard was born. RS-485 adopts balanced transmission and differential reception, and has the ability to suppress common mode interference. In addition, the bus transceiver has high sensitivity and can detect voltages as low as 200mV, so that the transmission signal can be recovered outside the kilometer. RS-485 adopts Half-duplex working mode, which can be networked to form a distributed system, is very convenient for multi-point interconnection, can save many signal lines, and allows up to 32 drives and 32 receivers in parallel.
USB: Universal Serial Bus is an external bus standard that supports plug-and-play and hot-swap functions of devices. It has the advantages of fast transmission speed, convenient use, flexible connection and independent power supply. USB uses a 4-pin (USB 3.0 standard 9-pin) plug as a standard plug. It can be daisy-chained to connect all peripherals, and can connect up to 127 external devices without losing bandwidth. Can be connected to keyboard, mouse, printer, scanner, camera, charger, flash drive, mobile hard drive, external optical drive / floppy drive, USB network card, ADSL Modem, Cable Modem, MP3 player, mobile phone, digital camera, etc. almost all external equipment. It has successfully replaced the serial port and the parallel port, and has become one of the mandatory interfaces for personal computers and smart devices.

Information is transmitted between devices using wireless signals. There are mainly wireless RF433/315M, Bluetooth, Zigbee, Z-ware, IPv6/6Lowpan.
RF433/315M: wireless transceiver module, using RF technology, working in ISM band (433/315MHz), generally including transmitter and receiver, high frequency stability, good harmonic suppression, data transmission rate 1K ~ 128Kbps, using The modulation mode of GFSK has superior anti-interference ability. Applications: (1) Wireless meter reading system (2) Wireless street light control system (3) Railway communication (4) Model wireless remote control (5) Wireless security alarm (6) Home appliance control (7) Industrial wireless data collection (8) Wireless data transmission. The low-power RF433 can operate in the voltage range of 2.1-3.6V. In the 1SEC cycle polling mode, the charging mode consumes less than 20uA, and a 3.6V/3.6A lithium-ion battery can be used. Work for more than 10 years.
Bluetooth: UHF radio waves in the ISM band of 2.4 to 2.485 GHz, packet-based, wireless technology standards with master-slave architecture, enabling short-distance between fixed devices, mobile devices, and building personal area networks Data exchange. Managed by the Bluetooth Technology Alliance (SIG), the IEEE lists Bluetooth technology as IEEE 802.15.1, but it is no longer maintained. Bluetooth technology has a proprietary network that can be distributed to standards-compliant devices. Bluetooth uses frequency hopping technology to split the transmitted data into packets and transmit the packets separately through 79 designated Bluetooth channels. Each channel has a bandwidth of 1 MHz. Bluetooth 4.0 uses 2 MHz spacing and can accommodate up to 40 channels. A good quality wireless Bluetooth headset battery can be used for 2-3 years, usually several weeks.
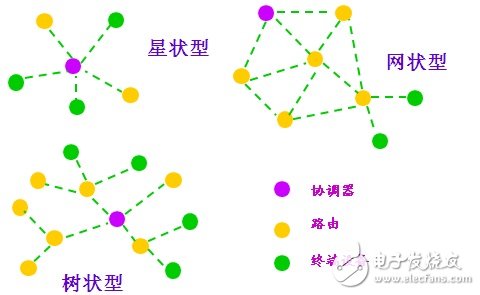
Zigbee: is a LAN communication protocol based on the IEEE802.15.4 standard for low-speed, short-distance, low-power, two-way wireless communication technology, also known as the Zigbee protocol. Features are close range, low complexity, self-organizing (self-configuration, self-healing, self-management), low power consumption, low data rate. From the bottom to the top, the ZigBee protocol is the physical layer (PHY), the medium access control layer (MAC), the transport layer (TL), the network layer (NWK), the application layer (APL), etc., where the physical layer and the medium access control layer follow The IEEE 802.15.4 standard is mainly used for sensor control applications (Sensor and Control). It can work in 2.4GHz (global popular), 868MHz (popular in Europe) and 915MHz (popular in the US), with transmission rates up to 250kbit/s, 20kbit/s and 40kbit/s, respectively. In the range of 10-75m, ZigBee can be a wireless data transmission network platform consisting of 65535 wireless data transmission modules. Each ZigBee network data transmission module can communicate with each other from the standard 75m. The distance is unlimited. The ZigBee node is very power efficient, with battery life of up to 6 months to 2 years, and up to 10 years in sleep mode. The following figure is a network diagram of Zigbee (this image is from the Internet):
Z-Wave: is a radio-based, low-cost, low-power, high-reliability, network-suitable short-range wireless communication technology led by the Danish company Zensys. The operating band is 908.42MHz (USA) ~ 868.42MHz (Europe ), using FSK (BFSK/GFSK) modulation, the data transmission rate is 9.6 kb~ 40kb/s, the effective coverage of the signal is 30m indoors, and the outdoor can exceed 100m, suitable for narrow broadband applications. Z-Wave uses dynamic routing technology. Each Z-Wave network has its own independent network address (HomeID); the address (NodeID) of each node in the network is assigned by the control node (Controller). Each network can accommodate up to 232 nodes (Slave), including control nodes. Zensys provides a Dynamically Linked Library (DLL) for Windows development. The developer uses the API functions in the DLL for PC software design. The wireless network built by Z-Wave technology can not only remotely control home appliances through the network equipment, but also control devices in the Z-Wave network through the Internet.
IPv6/6Lowpan: IPv6-based low-speed wireless personal area network standard, namely IPv6 over IEEE 802.15.4. The IEEE 802.15.4 standard is designed to develop compact low-power, inexpensive embedded devices (such as sensors) that can run on batteries for one to five years. The standard uses a radio transceiver operating in the 2.4 GHz band to transmit information using the same frequency band as Wi-Fi, but its RF transmit power is only about 1% of Wi-Fi. The emergence of 6LoWPAN enables various low-power wireless devices to join the IP home, and is connected to Wi-Fi, Ethernet and other types of devices; IETF 6LoWPAN technology has the characteristics of wireless low-power, self-organizing network, is the Internet of Things perception Layers, important technologies of wireless sensor networks, ZEPBee's new generation of smart grid standards SEP2.0 has adopted 6LoWPAN technology, with the deployment of the US smart grid, 6LoWPAN will become the de facto standard, a comprehensive replacement for the ZigBee standard.
3. Traditional InternetSince the development of the Internet to the present, basically all software systems are running on the Internet. People get all kinds of data from the Internet, communicate and work. Basically everyone knows the Internet. Here is a brief description.
WIFI: A wireless LAN based on the IEEE 802.11 standard can be regarded as a short-range wireless extension of a wired LAN. Setting up a WIFI requires only one wireless AP or a wireless router, and the cost is low.
Ethernet: Includes standard Ethernet (10Mbit/s), Fast Ethernet (100Mbit/s) and 10G (10Gbit/s) Ethernet. They are all compliant with IEEE 802.3, which specifies the content of the physical layer's wiring, electrical signals, and media access layer protocols.
Mobile wireless communication technology has developed to the present, mobile terminals directly access the Internet world. With the decline of communication tariffs and the cost of 3G/4G wireless modules, 3G/4G can easily communicate directly with the Internet, and more and more devices are adopted. Mobile network technology.
3G/4G: The third and fourth generation mobile communication technologies, 4G is a combination of 3G and WLAN, capable of transmitting data, images, audio, video, etc. quickly and with high quality. 4G can be deployed in a place where the wired network does not cover, and can be downloaded at a speed of more than 100 Mbps, which can meet the requirements of almost all users for wireless services, and has incomparable superiority. The 4G mobile system network structure can be divided into three layers: physical network layer, intermediate environment layer, and application network layer.
Article reference program life blog
Anisotropic Ferrite Magnets y35,Custom Anisotropic Ferrite Magnets Y25,Barium Ferrite Magnets Y10T,Ferrite Disk Magnets 20mm
HU NAN YUBANG MAGNETIC MATERIAL CO.,LTD , https://www.ybmagnet.com
